Polar Bonds and Electronegativity
When two identical atoms form a covalent bond, as in H2
or Cl2, each has an equal share of the electron pair in the
bond. The electron density at both ends of the bond is the same, because
the electrons are equally attracted to both nuclei.
When different kinds of atoms combine, as in HCl, the attractions
usually are not equal. Generally one of the nuclei attracts the
electrons more strongly than the other.
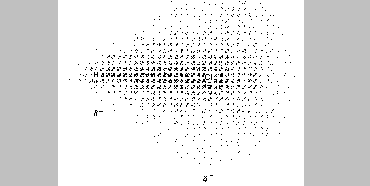
The effect of unequal attractions for the bonding electrons is an
unbalanced distribution of electron density within the bond. It has been
found that a chlorine atom attracts the electrons more strongly than
does a hydrogen. In the HCl molecule, therefore, the electron cloud is
pulled more tightly around the Cl, and that end of the molecule
experiences a slight buildup of negative charge. The electron density
that shifts toward the chlorine atom is removed from the hydrogen, which
causes the hydrogen end to acquire a slight positive charge.
In HCl the electron transfer is incomplete. The electrons are
still shared, but unequally. The charges on either end of the molecule
are less than full +1 and -1 charges; they are partial charges, normally
indicated by the lowercase Greek letter delta.
A bond that carries partial positive and negative charges on
opposite ends is called a polar bond, or polar covalent bond. The term
polar comes from the notion of poles of opposite charge at either
end of the bond. Because there are two poles of charge involved, the
bond is said to be a dipole.
The polar bond in HCl causes the molecules as a whole to have
opposite charges on either end, so we say that HCl is a polar molecule.
The HCl molecule as a whole is also a dipole.
The degree to which a covalent bond is polar depends on the
relative abilities of bonded atoms to attract electrons. The term that
we use to describe this relative attraction of an atom for the electrons
in a bond is called the electronegativity of the atom. In HCl the
chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen. The electron pair of the
covalent bond spends more of its time around the more electronegative
atom, which is why that end of the bond acquires a partial negative
charge.
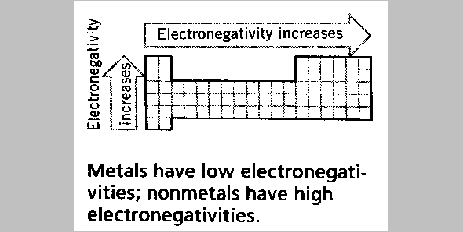
The concept of electronegativity has been put on a quantitative
basis - as numerical values have been assigned for each element. Refer
to your periodic table for these assigned values. This information is
useful because the difference in electronegativity values
provides an estimate of the degree of polarity of a bond. In addition,
the relative magnitudes of the electronegativities indicate which end of
the bond carries the negative charge. For instance, fluorine is more
electronegative than chlorine. Therefore, we would expect an HF molecule
to be more polar than an HCl molecule. In addition, hydrogen is less
electronegative than either fluorine or chlorine, so in both of these
molecules the hydrogen bears the positive charge.
.. ..
H-F: H-Cl:
.. ..
+ - + -
The concept of electronegativity shows that there is no sharp
dividing line between ionic and covalent bonding.
Ionic bonding and nonpolar covalent bonding simply represent the
two extremes. Ionic bonding occurs when the difference in
electronegativity between two atoms is very large; the more
electronegative atom acquires essentially complete control of the
bonding electrons. In a nonpolar covalent bond, there is no difference
in electronegativity, so the pair of bonding electrons is shared
equally.
The degree of polarity, which is the amount of ionic character of
the bond varies in a continuous way with changes in the
electronegativity difference. The bond becomes more than 50% ionic
when the electro-negativity difference exceeds 1.7
Within the periodic table, electronegativity varies in a more of
less systematic way, and the trends follow those for the ionization
energy (IE). Atoms with large ionization energies also have large
electronegativities. An atom that has a small IE will give away an
electron more easily than an atom with a large IE, just as an atom with
a small electronegativity will lose its share of an electron pair more
readily than an atom with a large electronegativity.
|

