| Ground Water |
Preface
As the salesmen sang in the musical The Music Man, "You gotta know
the territory." This saying is also true when planning to buy or build a house.
Learn as much as possible about the land, the water supply, and the septic
system of the house before buying or building. Do not just look at the
construction aspects or the beauty of the home and surroundings. Be sure to
consider the environmental conditions around and beneath the site as well. Try
to visit the site under adverse conditions, such as during heavy rain or
meltwater runoff, to observe the drainage characteristics, particularly the
condition of the basement.
Many of the conditions discussed in this book, such as lowered well-water
levels, flooded basements, and contamination from septic systems, are so common
that rural families often have to deal with one or more of them. The purpose of
this book is to awaken an interest in ground water and an awareness of where it
is available, how it moves, how people can adjust to its patterns to avoid
problems, and how it can be protected and used wisely.
This booklet provides both present and prospective rural homeowners,
particularly those in the glaciated northern parts of the United States, with a
basic but comprehensive description of ground water. It also presents problems
one may expect to encounter with ground water and some solutions or suggestions
for help with these problems.
Introduction
When buying a home in the country, people need to consider certain factors
that usually do not confront the urban homebuyer, such as whether or not the
water supply is adequate and if the means of disposing of wastewater is safe.
Disappointed rural homeowners have sometimes found out too late that the well
drilled on their new land does not yield enough water or that the water is of
poor chemical quality. Also, foundations can become unstable from excess surface
runoff or from high ground-water levels. Septic systems, if not located properly
or if soil conditions are not properly considered, can fail. Wells can be
contaminated by septic systems or barnyard wastes. Shallow or dug wells on farms
or near older homes that served adequately in earlier years are often inadequate
for modern uses.
Preventing water problems or coping with them when buying or building a rural
home can be either complex or relatively simple. Prospective homeowners need to
know about the terrain, the proximity of the house to other structures, and the
condition of the existing well and septic system. If building in an unpopulated
area, drill a well first�or if buying an old house, find out if the water supply
is adequate. This booklet describes the most common well problems encountered by
rural homeowners, how to recognize them, solve them, or get help. But first, the
characteristics and behavior of ground water and the relationship between ground
water and the surrounding land are discussed briefly.
The Hydrologic Cycle
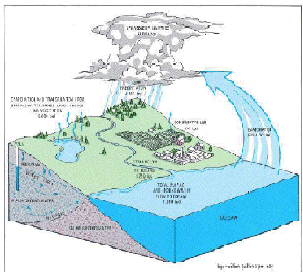
The continuous hydrologic cycle.
The hydrologic cycle is the continuous circulation of water from land and sea
to the atmosphere and back again : water evaporates from oceans, lakes, and
rivers into the atmosphere. This water later precipitates as rain or snow onto
the land where it evaporates or runs off into streams and rivers ; or it
infiltrates (seeps) into the soil and rock from which some is transpired back
into the atmosphere by plants. The remainder becomes ground water, which
eventually seeps into streams or lakes from which it evaporates or flows to the
oceans.
Ground Water
Ground water is that part of precipitation that infiltrates through the soil
to the water table. The unsaturated material above the water table contains air
and water in the spaces between the rock particles and supports vegetation. In
the saturated zone below the water table, ground water fills in the spaces
between rock particles and within bedrock fractures.
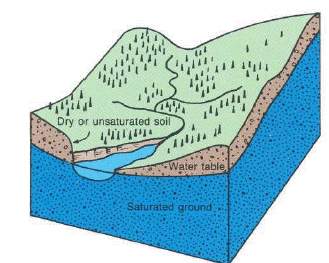
Occurrence of ground water.
Where ground water occurs
Rock materials may be classified as consolidated rock (often called bedrock)
and may consist of sandstone, limestone, granite, and other rock, and as
unconsolidated rock that consists of granular material such as sand, gravel, and
clay. Two characteristics of all rocks that affect the presence and movement of
ground water are porosity (size and amount of void spaces) and
permeability (the relative ease with which water can move through spaces in
the rock).
Consolidated rock may contain fractures, small cracks, pore spaces, spaces
between layers, and solution openings, all of which are usually connected and
can hold water. Bedded sedimentary rock contains spaces between layers that can
transmit water great distances. Most bedrock contains vertical fractures that
may intersect other fractures, enabling water to move from one layer to another.
Water can dissolve carbonate rocks, such as limestone and dolomite, forming
solution channels through which water can move both vertically and horizontally.
Limestone caves are a good example of solution channels. Consolidated rock may
be buried below many hundred feet of unconsolidated rock or may crop out at the
land surface. Depending upon the size and number of connected openings, this
bedrock may yield plentiful water to individual wells or be a poor water-bearing
system.
Unconsolidated material overlies bedrock and may consist of rock debris
transported by glaciers or deposited by streams or deposited in lakes. It also
may consist of weathered bedrock particles that form a loose granular or clay
soil. Well-sorted unconsolidated material can store large quantites of ground
water; the coarser materials�sand and gravel�readily yield water to wells.

How ground water occurs in rocks.
A close look at the rocks exposed in road cuts and along streams will show
the types of openings in which ground water can occur. Especially noticeable in
bedrock exposures are spaces between layers that can extend for miles-the void
spaces between rock particles contain water that percolates into these spaces
between the layers. In most sand and gravel deposits, water occupies and moves
freely within granular material.

Road cuts reveal fractures, joints, and bedding planes.
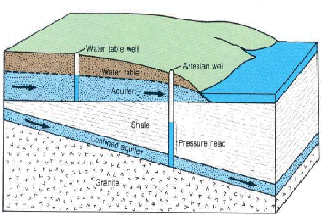
Water-table and confined (artesian) aquifers.
Aquifers
Most of the void spaces in the rocks below the water table are filled with
water. Wherever these water-bearing rocks readily transmit water to wells or
springs, they are called aquifers.
Although ground water can move from one aquifer into another, it generally
follows the more permeable pathways within the individual aquifers from the
point of recharge (areas where materials above the aquifer are permeable enough
to permit infiltration of precipitation to the aquifer) to the point of
discharge (areas at which the water table intersects the land surface and water
leaves an aquifer by way of springs, streams, or lakes and wetlands). Where
water moves beneath a layer of clay or other dense, low-permeability material,
it is effectively confined, often under pressure. The pressure in most confined
aquifers causes the water level in a well tapping the aquifer to rise above the
top of the aquifer. Where the pressure is sufficient, the water may flow from a
well.
Ground water is constantly moving
Ground water is always moving by the force of gravity from recharge areas to
discharge areas. Ground-water movement in most areas is slow-a few feet per
year. But, in more permeable zones, such as solution channels in limestone,
movement can be as much as several feet per day. Evidence of the movement of
ground water through rock and soil can be seen in road cuts, especially in
winter, when the water freezes upon emerging from the rock. In some bedrock
exposures, the water emerges along partings between rock layers ; in others,
along vertical fractures.
Seasonal patterns of ground-water recharge and storage
In latitudes where freezing is common, there is less recharge from rain or
snowmelt during winter, which causes the water table to fall. Sporadic or
differential freezing of the soil in the fall and winter inhibits recharge to
the saturated zone, and the complete freezing of the soil in winter prevents all
recharge until the soil thaws in the spring.
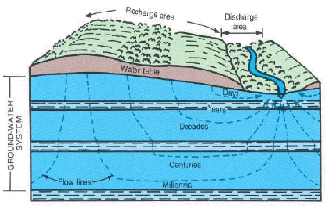
Direction and rate of ground-water movement.

Ground water, emerging from bedding planes, has created
spectacular frozen waterfalls along a road cut.
The saturated zone beneath the water table is recharged by the excess water
that is not discharged to streams. The resulting rise in the water table
increases ground-water storage (the volume of ground water stored
within an aquifer system). In late spring, summer, and early fall, evaporation
and transpiration by plants capture most of the water that would otherwise
recharge the aquifer, while discharge to streams continues. A seasonal decrease
in ground-water storage results, as indicated by declining water levels in
wells. In winter, freezing of the soil prevents recharge, which again causes a
decline in storage. In early spring, frequent precipitation coupled with water
from snowmelt causes a rapid increase in storage and a rise in the water table.
|

