Well, that was mildly amusing. We are now standing in a hot humid room and
have a warped pot laying upon the burner. But, on the bright side, we understand
the universe a little better and are one step closer to setting up a
distillation column. Now, lets put a mixture of liquids in a pot and
repeat the same experiment. We choose a bottle of whiskey, and pour it into the
pot. The whiskey is made of half ethanol (ethyl alcohol) and half
water. However, it is not entirely clear what is going to happen when we
heat the mixture, because pure ethanol boils at 173 degrees Fahrenheit
(78.3 degrees Celsius), not 212 degrees like pure water. Will the
temperature remain constant while the mixture boils off? With this question
in mind we eagerly turn on the burner and watch the thermometer. Our findings
are summarized below:
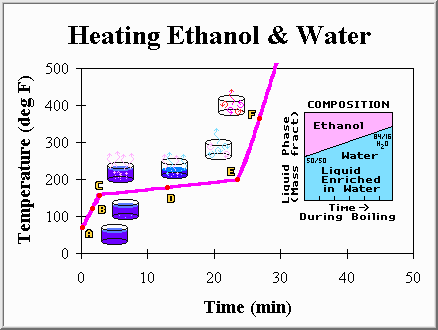
Point A: The mixture of ethanol and water has just been
placed on the burner. The liquid is still cool, and for a moment we consider
stopping the experiment to take a sip.
Point B: The mixture is warming up faster than the pure water
did. This is not too surprising as we know that pure ethanol would warm up much
faster than pure water. Ethanol's heat capacity (2.8 kJ/kg C) is smaller than
that of water, and we expect the ethanol-water mixture to have properties
somewhere between that of the pure components.
Point C: The first bubble appears at the bottom and rises to
the surface. If we could catch this bubble we would find that it is enriched
in ethanol. While the liquid is 50% ethanol and 50% water, the first bubble
of vapor is over 65% ethanol. This may come as a surprise, but makes some
sense... Because ethanol has a lower boiling point it has a tendency to boil off
first. This temperature (about 176 degrees Fahrenheit) is called the bubble
point, because it is the temperature at which the first bubble forms.
Point D: Ethanol, and water, continues to be boiled off.
However, the temperature is not remaining constant. Instead, it has
slowly been increasing. The latent heat is still present, and is
responsible for slowing the temperature rise, but its presence is not nearly as
obvious as when we had only pure water. The temperature is rising because the
liquid phase is being enriched in water, which has a higher boiling
point. This liquid enrichment occurs because the first vapors were mainly
ethanol, and so a larger fraction of water was left behind.
Point E: The last drop of liquid is very rich in water,
and it too eventually boils away. This is called the dew point because if
we were condensing the vapor instead of boiling the liquid this would be the
temperature at which the first drop of liquid would form (about 185 degrees
Fahrenheit). That first drop of liquid condensed would be mostly (84%) water.
Point F: The temperature of the vapors within the pot
continues to rise until they are as hot as the burner.
Summary of our findings:
Mixtures have a capacity to absorb heat, and in the process
become warmer.
Mixtures boil when they reach a temperature called their
bubble point. Afterwards the temperature slowly rises, even though latent
heat is still present, until the last drop of liquid vaporizes at the
dew point.
The vapor produced at the bubble point is rich in the lower
boiling compound (in this case ethanol).
The last little bit of liquid is rich in the higher boiling
compound (in this case water).
Once all the liquid is boiled off the temperature of the vapor
mixture will again increase.
Batch distillation
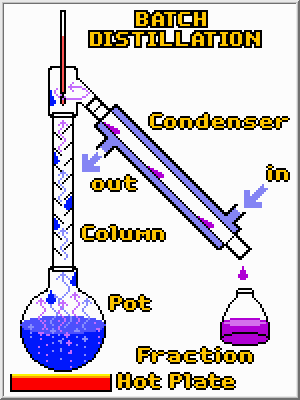
It is fairly easy to turn pots and burners into a batch
distillation apparatus. A condenser is required to turn the vapors
back to a liquid so they can be easily collected. A tall column is
also desirable because it greatly improves the separation by giving high boiling
compounds another chance to condense before they reached the top and are
collected. Finally, by using different collection vessels, the original
mixture can be separated into fractions. However, despite these bells and
whistles the principle is the same; by applying heat a distillation column
separates compounds in a mixture based upon their boiling points.
Continuous Distillation
One of the characteristics of the Industrial Revolution has been a
shift from small scale batch (craft like) operations to large
scale continuous (plant based) mass production. Ford's automotive
assembly line is the typical example of mass production, but the same
kinds of changes also occurred in the chemical industry. Labor intensive
batch distillation was replaced with continuous distillation
which allowed a much greater chemical throughput. Just as mass production
techniques greatly reduced the price of a "Model T" automobile, it
also greatly reduced the price of the gasoline which powered that
machine.
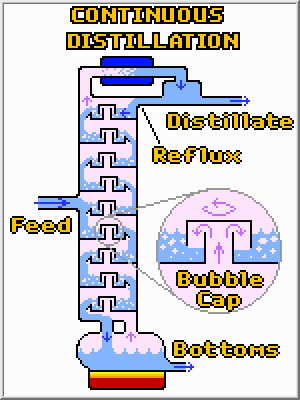
There are two major types of continuous distillation columns, but both
operate in basically the same way. In both cases liquid is
continuously fed into the column, and at least two streams (distillate
and bottoms), together containing the same amount of total material, are
continuously removed. Heat is added to the re-boiler
(pot) and removed at the condenser. The re-boiler vaporizes some
of the liquid, which then follows a treacherous path to the top of the column
where it is re-condensed. Along the way most of the high boiling compounds will
been left behind, and the distillate will be quite pure. To further aid
the separation process some of the liquid distillate is often returned to the
column where it flows back to the bottom. Along the way this reflux
condenses some of the higher boiling liquids out of the vapor phase helping to
purify the vapor. The two types of columns are:
Tray Columns (shown above): Such columns consist of physically
separated pools of liquid which are in intimate contact with a vapor. Bubble
columns are often used to force the upward flowing vapor through these pools of
downward flowing liquid. Each of these trays operates as an equilibrium stage
(like the pot and water examples above).
Packed Columns: Such columns are filled with a saddle shaped packing
that resembles Styrofoam peanuts. This packing provides a lot of surface area
for the vapor to condense upon and assures that the liquid and vapor are in
intimate contact.
Whereas the composition of the distillate and bottoms in batch
distillation changes over time, a continuous column operates under
steady conditions where the composition at a given location does not change
over time. This steady state operation is desired in almost all
continuous unit operations. Because the composition only depends upon the
position in the column, additional product steams can be easily tapped at
different heights (not shown) and each tray will have a different composition of
compounds. The trays at the top of the column are rich in light boiling
compounds while those at the bottom are rich in compounds that only boil at high
temperatures.
|

