We can also use reactive distillation with the reaction and
see if the conversion improves. Methyl Acetate will be the product that is
removed.
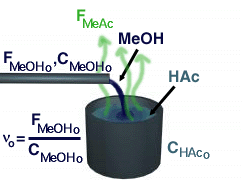
Reactive Distillation - Only Methyl Acetate Evaporates
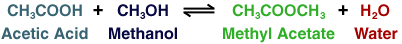
| Mole Balance |
|
|
| |
| |
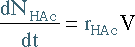 |
|
|
|
| |
| Mass Balance |
|
|
| |
 |
|
|
|
| |
| |
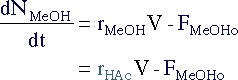 |
|
|
| |
| |
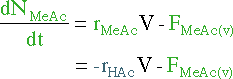 |
|
|
| |
| |
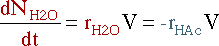 |
|
| |
| |
| Rate Law |
|
| |
| |
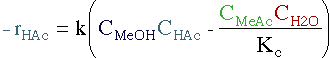 |
Unfortunatly we are not given an evaporation rate for methy
acetate, so we must look else where to find one. One such equation is :
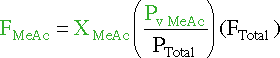
| FMeAc |
|
Rate at which Methyl Acetate is removed
from the reaction mixture by evaporation |
| XMeAc |
|
Mole fraction of reaction mixture that is
methyl acetate |
| Pv MeAc |
|
Vapor pressure of methyl acetate at reaction
temperature |
| PTotal |
|
Total pressure of the system |
| FTotal |
|
Rate at which air is bubbled through the
reactor. As the species evaporate, they will
be collected in the air bubbles. |
Now we need to figure out the vapor pressure of methyl
acetate. From Perry's Chemical Engineering Handbook, we can develop the
equation :
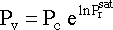
and that for methy acetate :
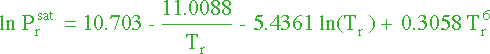
|