| Organic Chemistry |
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Introduction
A wide range of compounds existing either naturally or synthetically prepared
are known to possess the element carbon. This forms a branch of chemistry, known
as Organic Chemistry. Over three million different organic compounds have
been characterized & every year tens of thousands of new substances are added to
the list.

Antoine Lavoisier
In 1774, Antoine Lavoisier showed that compounds obtained from
vegetable and animal sources always contained at least carbon and hydrogen.
Carbon is not the only element found in organic compounds. Hydrogen atoms are
almost always present. In addition organic compounds often contain atoms of
oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur or the halogens. The bonds formed by carbon
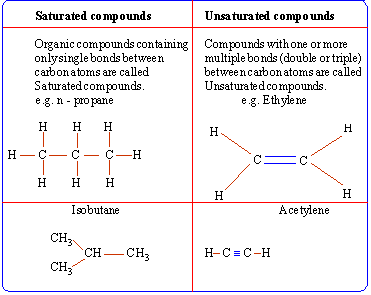
with other carbon atoms or other atoms can be single, double or triple bonds.
Standard conventions used to represent these bonds are as follows:
| No. of lines |
Type of bond |
Example |
| Single |
Single |
C - C, C
- H |
| Double |
double |
C = C, C = O |
| Triple |
triple |
C � C, C
� N |
Organic compounds differ considerably from
inorganic compounds. The following comparison illustrates the
difference between organic and inorganic compounds. Remember that
there are exceptions to every point of comparison
| |
Organic compounds
|
Inorganic
compounds |
| (i) |
Relatively few elements (mainly C, H, O, N,
S, P, F, Cl, Br, I) are involved. |
All elements are involved. |
| (ii) |
Bonds are covalent. |
Bonds are ionic or electrovalent. |
| (iii) |
Sparingly soluble or insoluble in water but
soluble in non-aqueous solvents (organic solvents). |
Soluble in water but insoluble in organic
solvents. |
| (iv) |
Volatile in nature. |
Non-volatile in nature. |
| (v) |
Non electrolytes |
Electrolytes |
| (vi) |
Rate of reaction is slow and a catalyst is
needed. |
Rate of reaction is fast and a catalyst is
not needed. |
| (vii) |
Mostly inflammable |
Not inflammable |
| (viii) |
Complex structure |
Simple structure |
| (ix) |
Isomerism is very common. |
Isomerism is not very common. |
|