ELECTROCHEMISTRY
Introduction
Electrochemistry is that branch of chemistry which deals with the
relationship between chemical energy and electrical energy. Chemical reactions
produce electrical energy and conversely, electrical energy can carry out
chemical reactions. These transformations take place through the flow of
electrons. Electrons are evolved at one place (oxidation), transferred through a
conductor (metal wire) and absorbed at another place (reduction).
A chemical reaction can generate electrical energy if it takes place
spontaneously, when carried out under appropriate conditions. Here conditions
mean proper device, concentration and temperature or pressure. The reaction of
zinc with copper sulfate is one such example which produces heat energy when
reacted upon in a simple vessel. But when the same reaction is carried out in a
special device called Daniell cell it produces electrical energy.
Reactions that do not take place spontaneously, can be made to take place by
applying an external source of electrical energy.
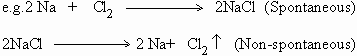
The former reaction generates heat (energy) whereas the latter reaction
requires electrical energy under appropriate conditions.
Electrochemistry finds its application in many fields like

|