SOLUTIONS
Solutions are homogenous mixtures. They may be classified according to
their physical state: gaseous, solid and liquid solutions.
Gaseous solutions, of which air is an example, are mixtures of
molecules of two or more gases.
Certain alloys are solid solutions e.g. Brass is a solid solution of
zinc and copper.
Liquid solutions are the most common.
8.1 Nature of Solution
Solutions are obtained when solutes are dissolved in solvents. The
component of the solution that is present in greater quantity is called the
solvent and the other component is called the solute.
The solubility of a substance in a particular solvent at a specified
temperature is the maximum amount of the solute that will dissolve in a definite
amount of the solvent and produce a stable system.
For a given solution, the amount of solute dissolved in a unit volume of
solution ( or unit amount of solvent ) is the concentration of the
solute.
The following figures show the solution of an ionic crystal in water. The
ions in the center of the crystal are attracted equally in all directions by
oppositely charged ions of the crystal.
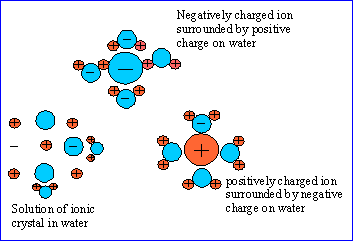
Solutions with a low concentration of solute are called dilute solutions
and those with a high concentration of solute are called concentrated
solutions.
If an excess of solute is added to the solvent then the equilibrium rate at
which the solute dissolves equals to the rate at which the solute
precipitates in the solution. Hence the amount of solute at a given time
remains constant and such solutions are called saturated solutions.
When less amount of solute is dissolved in a solvent it becomes an
unsaturated solution.
|