Ostwald’s Dilution Law
Ostwald’s dilution law is a relationship between the dissociation constant
and the degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte (acids, bases)
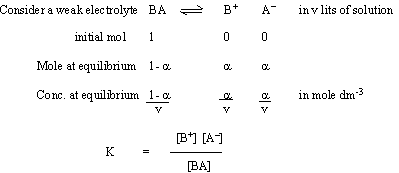
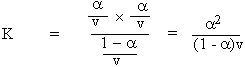
But concentration C = 1/v
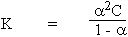
for a weak electrolyte a is very small ( and the
law does not apply to strong electrolytes)
\ K =
a2C
For a weak acid a =
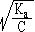
and a weak base a =
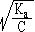
Examples : 1) The dissociation constant of a weak electrolyte is 4
+10-
5 Calculate the degree of dissociation in 0.1 m solution.
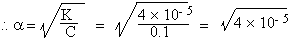
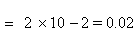
2) Calculate the [H+]
and degree of dissociation in 0.5 m solution of acetic acid (Ka
= 1.8´ 10-
5)
\
a = 6
´ 10- 3
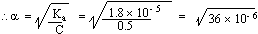
\a = 6
´ 10- 3
Now [H+] =
a C = 6
´ 10-
3 ´ 0.5
= 3 ´ 10- 3
m
|