4.6 Other Bonds
Metallic Bond :
In metals, the atoms are linked by a special type of bond called �metallic
bond�. It is suggested that the atoms in a metal free some of their electrons
and become positive ions. The matrix of positive ions remains embedded in a sea
of mobile electrons. The free electrons really cement the positive metal ions
and explain why metals are highly conductive of heat or electricity.
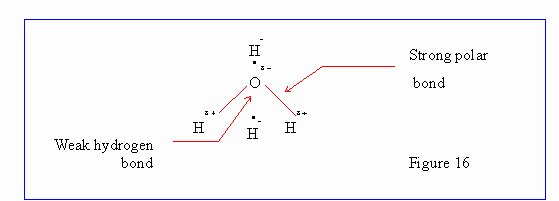
Hydrogen Bond :
Hydrogen atoms occuring in certain groups such as -OH carry some positive
charge and are thus attracted to electronegative atoms like oxygen and nitrogen
thereby making a link, called hydrogen bond, between two oxygen or nitrogen
atoms.
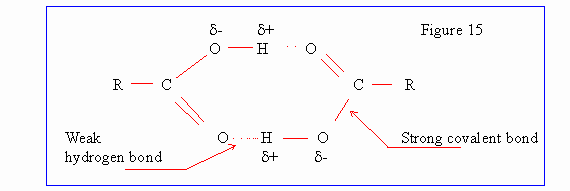
This hydrogen bond is electrostatic in nature and is not very strong. In ice
crystals we have a tetrahedral structure, each oxygen atom is surrounded by four
hydrogen atoms at the corner of the tetrahedron. Two of these are covalently
bond and other two form a hydrogen bond.
Van der Waal�s forces
These forces are the same as those existing between molecules in a real gas
leading to its non-ideality. The forces are really interatomic or
intermolecular, originating from dipole character. The forces are essentially
weak. They exist between lattice layers of graphite or mica, as also between
chains of selenium and tellurium.
|