Properties of Salts
1) Hydrolysis
This is a reaction in which a salt reacts with water to form a solution which
is either acidic or basic in nature.
a) Salt of weak alkali and strong acid
NH4Cl + H2O
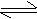 NH4OH
+ HCl NH4OH
+ HCl
(Slightly acidic)
b) Salt of strong alkali and weak acid
K2CO3 + H2O
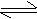 2KOH
+ H2CO3 2KOH
+ H2CO3
(Slightly basic)
c) Strong alkali and strong acid
NaCl + H2O Not hydrolyse
(neutral)
2) Efflorescence
The property of hydrated crystals to loose water of crystallization is called
efflorescence.
e.g. Washing soda ( Na2CO3 . 10 H2O )
Glauber�s salt ( Na2SO4 . 10 H2O )
Epson salt ( MgSO4 . 7 H2O )
3) Deliquescence
Certain salts when exposed to atmosphere, absorb moisture, becomes moist and
ultimately dissolve in absorbed water forming a saturated solution.
e.g. CaCl2.6H2O, FeCl3, NaOH
4) Hygroscopy
When a salt exposed to atmosphere, absorbs moisture without dissolving in it,
this property is called Hygroscopy.
e.g. Anhydrous CaCl2, Silica gel, CaO
|