GATE-2001
CE : CIVIL ENGINEERING
SECTION A
(75 Marks)
CE.l. This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-questions (1.1-1.25)
of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions four possible answers (A, B, C
and D) are given, out of which only one is correct. Answer each sub-question by
darkening the appropriate bubble on the OBJECTIVE RESPONSE SHEET (ORS) using a
soft HB pencil. Do not use the ORS for any rough work. You may use the Answer
Book for any rough work, if needed. (25 x 1 = 25)
1.1. The number of boundary conditions required to solve the following
differential equation is
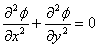
(a) 2 (c) 4
(b) 0 (d) 1
1.2. The value of the integral is I =
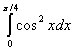
(a)
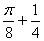
(b)
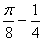
(c)
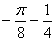
(d)
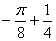
1.3. The limit of the following series as x approaches
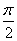 is
is
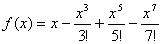
(a)
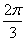 (b)
(b)
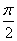
(c)
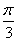 (d) 1
(d) 1
1.4. The degree of static indeterminacy, N s� and the degree of kinematic
indeterminacy, N k� for the plane frame shown below, assuming axial deformations
to be negligible, are given by
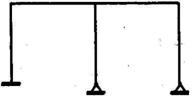 (a) N s = 6 and N k = 11
(a) N s = 6 and N k = 11
(b) N s = 6 and N k = 6
(c) N s = 4 and N k = 6
(d) N s = 4 and N k = 4
1.5. The bending moment (in kNm units) at the mid-span location X in the beam
with overhangs shown below-is equal to:
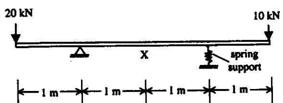
(a) 0
(b) - 1 0
(c) - 15
(d) -20
1.6. Identify the FALSE statement from the following, pertaining to the
effects due to a temperature rise D T in the bar BD alone in the plane truss
shown below:
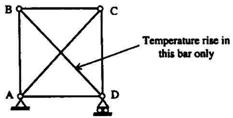
(a) No reactions develop at supports A and D.
(b) The bar BD will be subject to a tensile force.
(c) The bar AC will be subject to a compressive force.
(d) The bar BC will be subject to a tensile force.
1.7. Identify the correct deflection diagram corresponding to the loading in
the plane frame shown below:
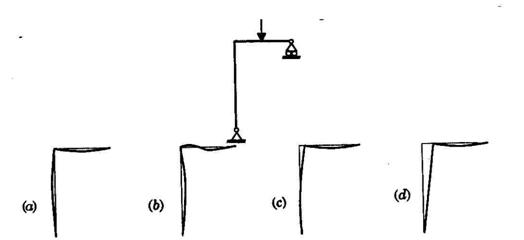
1.8. Identify the FALSE statement from the following, pertaining to the
methods of structural analysis:
- Influence lines for stress resultants in beams can be drawn using Miller
Breslau's Principle.
- The Moment Distribution Method is a force method of analysis, not a
displacement method.
- The Principle of Virtual Displacements can be used to establish a
condition of equilibrium. .
- The Substitute Frame Method is not applicable to frames subject to
significant sideway.
1.9. Identify the FALSE statement from the following, pertaining to the
design of concrete structures:
- The assumption of a linear strain profile in flexure is made use of in
working stress design, but not in ultimate limit state design.
- Torsional reinforcement is not required to be provided at the coners of
simply supported rectangular slabs, if the coners are free to lift up.
- A rectangular slab, whose length exceeds twice its width, always behaves
as a two-way slab, regardless of the support conditions.
- The 'load balancing' concept can be applied to select the appropriate
tendon profile in a prestressed concrete beam subject to a given pattern of
loads.
1.10. Identify the most efficient butt joint (with double cover plates) for a
plate in tension from the patterns (plan views) shown below, each comprising 6
identical bolts with the same pitch and gauge:
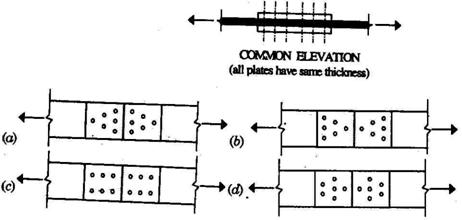
1.11. The following two statements are made with respect to different sand
samples having the same relative density. Identify if they are TRUE or FALSE.
I. Poorly graded sands will have lower friction angle than the well graded
sands.
II. The particle size has no influence on the friction angle of sand.
(a) II is TRUE but I is FALSE (b) Both are FALSE statements
(c) Both are TRUE statements. (d) I is TRUE but II is false.
1.12. The following two statements are made with reference to the calculation
of net bearing capacity of a footing in pure clay soil ( f = 0) using Terzaghi's
bearing capacity theory. Identify if they are TRUE or FALSE.
I. Increase in footing width will result in increase in bearing capacity.
II. Increase in depth of foundation will result in higher bearing capacity.
(a) Both statements are TRUE (b) Both statements are FALSE
(c) I is TRUE but II is FALSE (d) I is FALSE but II is TRUE
1.13. The width and depth of a footing are 2 and 1.5 m respectively. The
water table at the site is at a depth of 3 m below the ground level. The water
table correction factor for the calculation of the bearing capacity of soil is
(a) 0.875 (b) 1.000
(c) 0.925 (d) 0.500
1.14. The void ratio and specific gravity of a soil are 0.65 and 2.72
respectively. The degree of saturation (in percent) corresponding to water
content of 20% is
(a) 65.3 (b) 20.9
(c) 83.7 (d) 54.4
1.15. With respect to a c- f soil in an infinite slope, identify if the
following two statements are TRUE or FALSE.
I. The stable slope angle can be greater than f
II: The factor of safety of the slope does not depend on the height soil in
the slope.
(a) Both statements are FALSE (b) I is TRUE but II is FALSE
(c) I is FALSE but II is TRUE (d) Both statements are TRUE
1.16. In the Bernoulli equation. used in pipe flow. each term represents
(a) Energy per unit weight (b) Energy per unit mass
(c) Energy per unit volume (d) Energy per unit flow length
1.17. The stage-discharge relation in a river during the passage of flood is
measured. If q f is the discharge at the stage when water surface is falling and
q r is the discharge at the same stage when water surface is rising, then
(a) q f= q r (b) q f < q r
(c) q f > q r (d)
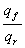 = constant for all stages
= constant for all stages
1.18. lsopleths are lines on a map through points having equal depth of
(a) Rainfall (b) Infiltration
(c) Evapotranspiration (d) Total runoff
1.19. A linear reservoir is one in which
(a) Storage varies linearly with time
(b) Storage varies linearly with outflow rate
(c) Storage varies linearly with inflow rate
(d) Storage varies linearly with elevation
1.20. Aeration of water is done to remove
(a) Suspended Impurities (b) Colour
(c) Dissolved Salts (d) Dissolved Gases
1.21. The following chemical is used for coagulation.
(a) Ammonium Chloride. (b) Aluminium Chloride.
(c) Aluminium Sulphate. (d) Copper Sulphate.
1.22. The unit in which both sedimentation and digestion processes of sludge
take place simultaneously is
(a) Skimming Tank (b) Imhoff Tank
(c) Detritus Tank (d) Digestion Tank
1.23. The design value of lateral friction coefficient on highway is
(a) 1.5 (b) 0.50
(c) 0.35 (d) 0.15
1.24. Camber on highway pavement is provided to take care of
(a) Centrifugal Force. (b) Drainage.
(c) Sight Distance (d) Off-Tracking.
1.25 The minimum value of CBR (%) required for granular sub-base as per
Ministry of Surface Transport (MOST) specification is
(a) 5 (b) 10
(c) 15 (d) 20
CE.2. This question consists of Twenty Five sub-questions (2.1.-2.25)
of TWO marks each. For each of these sub-questions four possible answers (A, B,
C and D) are given, out of which only one is correct. Answer each sub-question
by darkening the appropriate bubble on the OBJECTIVE RESPONSE SHEET (ORS) using
a soft HB pencil. Do not use the ORS for any rough work. You may use the Answer
Book for any rough work, if needed. (25 x 2 = 50)
2.1. Determinant of the following matrix is
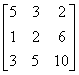
(b) � 28
(c) + 28
(d) + 72
2.2. The inverse Laplace Transform of
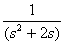 is,
is,
(a)
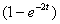 (b)
(b)
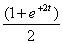
(c)
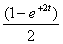 (d)
(d)
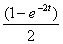
2.3. The solution for the following differential equation with boundary
conditions
y(0) = 2 and y'(1) =- 3 is,
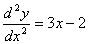
(a)
 (b)
(b)
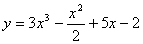
(c)
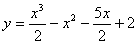 (d)
(d)
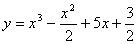
2.4. The product [p][Q] T of the following two matrices [P] and [Q] is
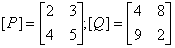
(a)
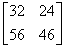 (b)
(b)
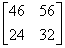
(c)
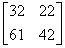 (d)
(d)
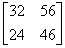
2.5. The given values of the matrix
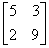 are,
are,
(a) (5.13,9.42) (b) (3.85,2.93)
(c) (9.00,5.00) (d) (10.16,3.84)
2.6. The frame below shows three beam elements OA, OB and OC, with identical
length L and flexural rigidity El, subject to an external moment M applied at
the rigid joint O. The correct set of bending moments {M OA' M oB' M oc} that
develop at O in the three beam elements OA, OB and OC respectively, is:
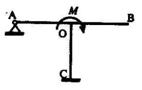
El/Lis constant for all three members
(a) {3M/8, M/8, 4M/8} (b) {3M/11, 4M/11, 4M/11}
(c) { M/3, M/3, M/3} (d) {3M/7, 0, 4M/7}
2.7. Identify, from the following, the correct value of the bending moment M
A (in kNm units) at the fixed end A in the statically determinate beam shown
below (with internal hinges at B and D), when a uniformly distributed load of 10
kN/m is placed on all spans. (Hint: Sketching the influence line for M A or
applying the Principle of Virtual Displacements makes the solution easy).
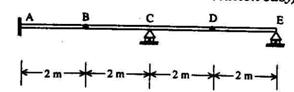
(a) -80 (b) -40
(c) 0 (d) + 40
2.8. The end moment (in kNm units) developed in the roof level beams in the
laterally loaded frame shown below (with all columns having identical
cross-sections), according to the Cantilever Method of simplified analysis, is :
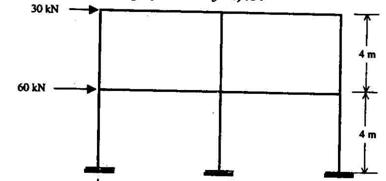
(a) 7.5 (b) 15
(c) 20 (d) 30
2.9. Consider the following two statements related to reinforced concrete
design, and
identify whether they are TRUE or FALSE:
I. Curtailment of bars in the flexural tension zone in beams reduces the
shear strength at the cut-off locations.
II. When a rectangular column section is subject to biaxially eccentric
compression, the neutral axis will be parallel to the resultant axis of bending.
(a) Both statements I and II are TRUE.
(b) Statement I is TRUE, and statement II is FALSE.
(c) Statement I is FALSE, and statement II is TRUE.
(d) Both statements I and II are FALSE.
2.10. Consider the following two statements related to structural steel
design, and identify whether they are TRUE or FALSE:
I. The Euler buckling load of a slender steel column depends on the yield
strength of steel.
II. In the design of laced column, the maximum spacing of the lacing does not
depend on the slenderness of column as a whole.
(a) Both statements I and II are TRUE.
(b) Statement I is TRUE, and statement II is FALSE.
(c) Statement I is FALSE, and statement II is TRUE.
(d) Both statements I and II are FALSE.
2.11. Identify the two FALSE statements from the following four statements.
I. The consolidation of soil happens due to the change in total stress.
II. When Standard Penetration Tests are performed in fine sands below the
water table, the dilation correction is applied after the overburden correction
is applied.
III. Over consolidated clays will have predominantly cohesive strength as
compared to the frictional strength.
IV. Compaction of soils is due to expulsion of water.
(a) II & III (b) I & IV
(c) I & III (d) II & IV
2.12. The critical slip circle for a slope is shown below along with the soil
properties.
The length of the arc of the slip circle is 15.6m and the area of soil within
the slip circle is 82 m 2. The radius of the slip circles is 10.3 m. The factor
of safety against the slip circle failure is nearly equal to,
(a) 1.05 (b) 1.22
(c) 0.78 (d) 1.28
2.13. The coefficients of permeability of a soil in horizontal and vertical
directions are 3.46 and 1.5 m/day respectively. The base length of a concrete
dam resting in this soil is 100 m. When the flow net is developed for this soil
with 1 : 25 scale factor in the vertical direction, the reduced base length of
the dam will be
(a) 2.63 m (b) 4.00 m
(c) 6.08 m (d) 5.43 m
2.14. A plate load test was conducted in sand on a 300 mm diameter plate. If
the plate settlement was 5 mm at a pressure of 100 kPa, the settlement (in mm)
of a 5 m x 8 m rectangular footing at the same pressure will be
(a) 9.4 (b) 18.6
(c) 12.7 (d) 17.8
2.15. Identify the two TRUE statements from the following four statements.
I. Negative skin friction is higher on floating piles than on end bearing
piles.
II. All other things being the same in footings on sand, the footing with
smaller
width will have lower settlement at the same net pressure.
III. The void ratio of soils is always less than 1.0.
IV. For determining the depth of embedment of anchored sheet piles, net
moment
at the anchor elevation is set to zero.
(a) I & IV (b) I & III
(c) II & IV (d) II & III
2.16. A 15 cm length of steel rod with relative density of 7.4 is submerged
in a two layer fluid. The bottom layer is mercury and the top layer is water.
The height of top surface of the rod above the liquid interface in 'cm' is
(a) 8.24 (b) 7.82
(c) 7.64 (d) 7.38
2.17. The direct runoff hydrograph of a storm obtained from a catchment is
triangular in shape and has a base period of 80 hours. The peak flow rate is 30
m 3/sec and catchment area is 86.4 km 2. The rainfall excess that has resulted
the above hydrograph is
(a) 5 cm (b) 8 cm
(c) 10 cm (d) 16 cm
2.18. A field was supplied water from an irrigation tank at a rate of 120
lit/see to irrigate an area of 2.5 hectares. The duration of irrigation is 8
hours. It was found that the actual delivery at the field, which is about 4 km
from the tank, was 100 lit/sec. The runoff loss in the field was estimated as
800 m 3. The application efficiency in this situation is
(a) 62% (b) 72%
(c) 76% (d) 80%
2.19. A trapezoidal channel with bottom width of 3m and side slope of IV:1.5H
carries a discharge of 8.0 m 3/sec with the flow depth of 1.5m. The Froude
number of the flow is
(a) 0.066 (b) 0.132
(c) 0.265 (d) 0.528
2.20. In a 1/50 model of a spillway, the discharge was measured to be 0.3 m
3/sec. The
corresponding prototype discharge in m 3/sec is
(a) 2.0 (b). 15.0
(c) 106.0 (d) 5303.0
2.21. If the BOD 5,20 of waste is 150mg/L and the reaction rate constant (to
the base 'e')
at 20�C is 0.35/day, then the ultimate BOD in mg/L is �
(a) 97.5 (b) 181.5
(c) 212.9 (d) 230.5
2.22. The Ca 2+ concentration and Mg 2+ concentration of a water sample are
160 mg/lit and 40 mg/lit as their ions respectively. The total hardness of this
water sample in terms of CaCO 3 in mg / lit is approximately equal to
(a) 120 (b) 200
(c) 267 (d) 567
2.23. A town has an existing horizontal flow sedimentation tank with an
overflow rate of 17m 3/day/m 2, and it is desirable to remove particles that
have settling velocity of 0.1mm/sec. Assuming the tank is an ideal sedimentation
tank, the percentage of particles removal is approximately equal to
(a) 30% (b) 50%
(c) 70% (d) 90%
2.24. A valley curve has a descending gradient of 1 in 40 followed by an
ascending� gradient of 1 in 50. The length of the valley curve required for a
design speed of 80 km/hour for comfort condition is
(a) 199 m (b) 116 m
(c) 58 m (d) 37 m
2.25. The radius of relative stiffness for a 20 cm thick slab with E = 3 x 10
5kg/cm 2 and Poisson's ratio = 0.15, resting on a subgrade having modulus of
5kg/cm 3 is
(a) 10 cm (b) 80 cm
(c) 120 cm (d) 320 cm

