Horn antenna
- an overview of the basics of the horn antenna used in RF microwave
applications.
The horn antenna is used in the transmission and reception of
RF microwave signals, and the antenna is normally used in conjunction with
waveguide feeds. The horn antenna gains its name from its appearance. The
waveguide can be considered to open out or to be flared, launching the signal
towards the receiving antenna.
Horn antennas are often used as gain standards, and as feeds
for parabolic or 'dish' antennas, as well as being used as RF antennas in their
own right. One particular use of horn antennas themselves is for short range
radar systems, such as those used for automotive speed enforcement.
When used as part of a parabolic reflector, the horn is
orientated towards the reflector surface, and is able to give a reasonably even
illumination of the surface without allowing radiation to miss the reflector. In
this way it is able to maximise the efficiency of the overall antenna. The use
of the horn antenna also minimizes the spurious responses of the parabolic
reflector antenna to signals that are not in the main lobe.
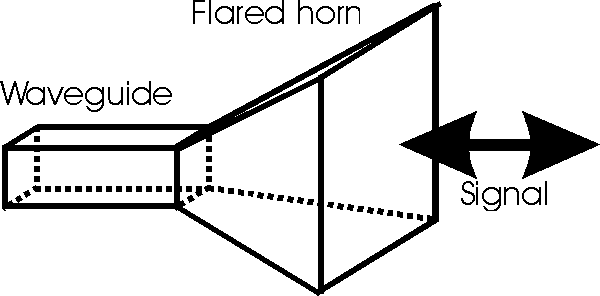
Horn antenna used for RF microwave applications
Basic horn antenna concept
The horn antenna may be considered as an RF transformer or
impedance match between the waveguide feeder and free space which has an
impedance of 377 ohms. By having a tapered or having a flared end to the
waveguide the horn antenna is formed and this enables the impedance to be
matched. Although the waveguide will radiate without a horn antenna, this
provides a far more efficient match.
In addition to the improved match provided by the horn
antenna, it also helps suppress signals travelling via unwanted modes in the
waveguide from being radiated.
However the main advantage of the horn antenna is that it
provides a significant level of directivity and gain. For greater levels of gain
the horn antenna should have a large aperture. Also to achieve the maximum gain
for a given aperture size, the taper should be long so that the phase of the
wave-front is as nearly constant as possible across the aperture. However there
comes a point where to provide even small increases in gain, the increase in
length becomes too large to make it sensible. Thus gain levels are a balance
between aperture size and length. However gain levels for a horn antenna may be
up to 20 dB in some instances.
Horn antenna types
There are two basic types of horn antenna: pyramid and
conical. The pyramid ones, as the name suggests are rectangular whereas the
corrugated ones are usually circular. The corrugated horn provides a pattern
that is nearly symmetrical, with the E and H plane beamwidths being nearly the
same. Additionally it is possible to control the side lobes better with a
conical or corrugated horn antenna.
Summary
The horn antenna is a particularly useful form of antenna for
use with RF microwave applications and waveguide feeder. Although it is not used
below RF microwave frequencies because waveguides are not used at low
frequencies as a result of the sizes needed, the horn antenna is nevertheless a
very useful form of RF antenna design for use at high frequencies.
|