Antenna polarisation or polarization
- overview, summary, tutorial about RF antenna or aerial polarisation and
the effect polarization has on RF antennas and radio communications.
Polarisation is an important factor for RF antennas and radio
communications in general. Both RF antennas and electromagnetic waves are said
to have a polarization. For the electromagnetic wave the polarization is
effectively the plane in which the electric wave vibrates. This is important
when looking at antennas because they are sensitive to polarisation, and
generally only receive or transmit a signal with a particular polarization. For
most antennas it is very easy to determine the polarization. It is simply in the
same plane as the elements of the antenna. So a vertical antenna (i.e. one with
vertical elements) will receive vertically polarised signals best and similarly
a horizontal antenna will receive horizontally polarised signals.
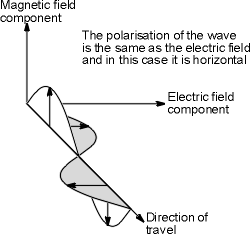
An electromagnetic wave
It is important to match the polarization of the RF antenna
to that of the incoming signal. In this way the maximum signal is obtained. If
the RF antenna polarization does not match that of the signal there is a
corresponding decrease in the level of the signal. It is reduced by a factor of
cosine of the angle between the polarisation of the RF antenna and the signal.
Accordingly the polarisation of the antennas located in free
space is very important, and obviously they should be in exactly the same plane
to provide the optimum signal. If they were at right angles to one another (i.e.
cross-polarised) then in theory no signal would be received.
For terrestrial radio communications applications it is found
that once a signal has been transmitted then its polarisation will remain
broadly the same. However reflections from objects in the path can change the
polarisation. As the received signal is the sum of the direct signal plus a
number of reflected signals the overall polarisation of the signal can change
slightly although it remains broadly the same.
Polarisation catagories
Vertical and horizontal are the simplest forms of antenna
polarization and they both fall into a category known as linear polarisation.
However it is also possible to use circular polarisation. This has a number of
benefits for areas such as satellite applications where it helps overcome the
effects of propagation anomalies, ground reflections and the effects of the spin
that occur on many satellites. Circular polarisation is a little more difficult
to visualise than linear polarisation. However it can be imagined by visualising
a signal propagating from an RF antenna that is rotating. The tip of the
electric field vector will then be seen to trace out a helix or corkscrew as it
travels away from the antenna. Circular polarisation can be seen to be either
right or left handed dependent upon the direction of rotation as seen from the
transmitter.
Another form of polarisation is known as elliptical
polarisation. It occurs when there is a mix of linear and circular polarisation.
This can be visualised as before by the tip of the electric field vector tracing
out an elliptically shaped corkscrew.
However it is possible for linearly polarised antennas to
receive circularly polarised signals and vice versa. The strength will be equal
whether the linearly polarised antenna is mounted vertically, horizontally or in
any other plane but directed towards the arriving signal. There will be some
degradation because the signal level will be 3 dB less than if a circularly
polarised antenna of the same sense was used. The same situation exists when a
circularly polarised antenna receives a linearly polarised signal.
Applications of antenna polarization
Different types of polarisation are used in different
applications to enable their advantages to be used. Linear polarization is by
far the most widely used for most radio communications applications. Vertical
polarisation is often used for mobile radio communications. This is because many
vertically polarized antenna designs have an omni-directional radiation pattern
and it means that the antennas do not have to be re-orientated as positions as
always happens for mobile radio communications as the vehicle moves. For other
radio communications applications the polarisation is often determined by the RF
antenna considerations. Some large multi-element antenna arrays can be mounted
in a horizontal plane more easily than in the vertical plane. This is because
the RF antenna elements are at right angles to the vertical tower of pole on
which they are mounted and therefore by using an antenna with horizontal
elements there is less physical and electrical interference between the two.
This determines the standard polarisation in many cases.
In some applications there are performance differences
between horizontal and vertical polarization. For example medium wave broadcast
stations generally use vertical polarisation because ground wave propagation
over the earth is considerably better using vertical polarization, whereas
horizontal polarization shows a marginal improvement for long distance
communications using the ionosphere. Circular polarisation is sometimes used for
satellite radio communications as there are some advantages in terms of
propagation and in overcoming the fading caused if the satellite is changing its
orientation.
|

