Waveguide basics tutorial
- overview, summary, tutorial about the basics of what is a waveguide and
the basic waveguide theory.
Waveguides are used in a variety of applications to carry
radio frequency energy from one pint to another. In their broadest terms a
waveguide is defined as a system of material that is designed to confine
electromagnetic waves in a direction defined by its physical boundaries. This
definition gives a very broad view of waveguides, and indeed waveguide theory is
used in a number of applications to provide waveguide applications in a number
of areas.
Typically a waveguide is thought if as a transmission line
comprising a hollow conducting tube, which may be rectangular or circular within
which electromagnetic waves are propagated. Unlike coaxial cable, there is no
centre conductor within the waveguide. Signals propagate within the confines of
the metallic walls that act as boundaries
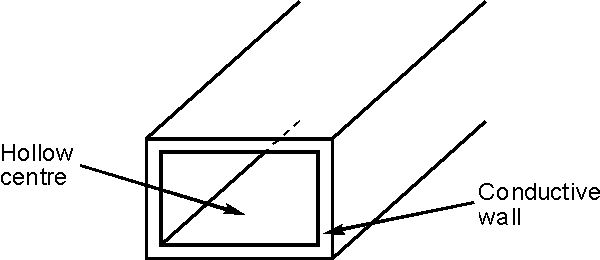
Rectangular waveguide
Waveguides will only carry or propagate signals above a
certain frequency, known as the cut-off frequency. Below this the waveguide is
not able to carry the signals. The cut-off frequency of the waveguide depends
upon its dimensions. In view of the mechanical constraints this means that
waveguides are only sued for microwave frequencies. Although it is theoretically
possible to build waveguides for lower frequencies the size would not make them
viable to contain within normal dimensions and their cost would be prohibitive.
Connecting signals to a waveguide
A signal can be entered into the waveguide in a number of
ways. The most straightforward is to use what is known as a launcher. This is
basically a small probe which penetrates a small distance into the centre of the
waveguide itself as shown. Often this probe may be the centre conductor of the
coaxial cable connected to the waveguide. The probe is orientated so that it is
parallel to the lines of the electric field which is to be set up in the
waveguide. An alternative method is to have a loop which is connected to the
wall of the waveguide. This encompasses the magnetic field lines and sets up the
electromagnetic wave in this way. However for most applications it is more
convenient to use the open circuit probe. These launchers can be used for
transmitting signals into the waveguide as well as receiving them from the
waveguide.
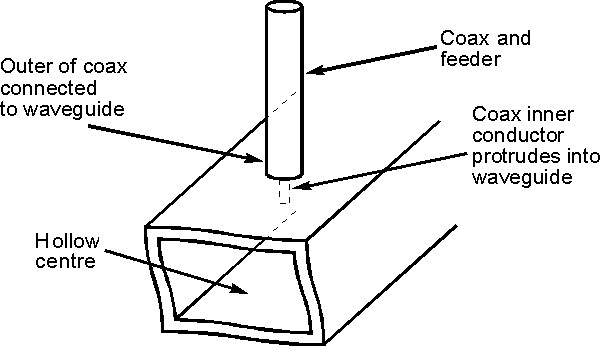
Waveguide launcher
|