Transistor current limiter
a simple one transistor circuit to act as a current limiter in a
power supply
A current limiting circuit is almost an essential element of
any modern power supply. There is always a risk that the power supply rails may
be shorted. The inclusion of a current limiter circuit will prevent any further
damage occurring to the external circuit as well as preventing damage to the
power supply itself.
It is possible to implement a power supply current limiter
with just diodes, but this one uses a single transistor and a current sense
resistor. This circuit forms the basis of most power supply current limiters
used today. The circuit is shown below incorporated into a simple regulator
circuit.
The operation of the current limiter is very straightforward.
When the power supply is supplying current below the maximum level, current
flows through the sense resistor and a small potential difference develops
across it. The value of the resistor is chosen so that at when the maximum
allowable current flows from the power supply, a voltage equal to the turn on
voltage of the current sense transistor is developed across it. This is
typically 0.6 volts, assuming that a silicon transistor is used.
As the voltage across the current sense resistor reaches 0.6
volts, so the current sense transistor starts to turn on. When it does this, the
voltage it the base of the main power supply pass transistor is pulled down,
thereby preventing any increase in the output current of the power supply. In
this way it is very easy to calculate the value for the sense resistor using
Ohms Law. It is simply 0.6 / maximum current. The current sense transistor
should have a sufficiently large current capacity to be able to take the current
the base of the main series pass transistor.
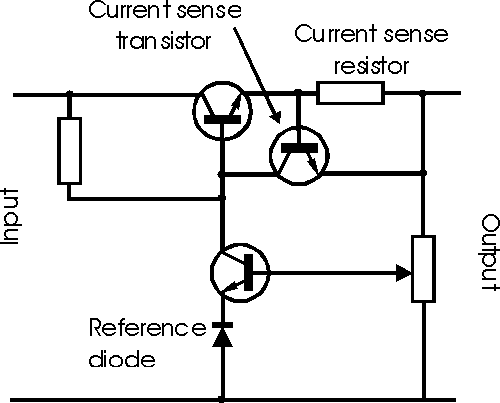
Power supply with feedback and transistor current
limiting
In view of the fact that the regulator sense point occurs
after the current sense resistor, any voltage drop across the resistor will not
affect the output voltage of the circuit as this will be compensated for by the
regulator. (This assumes that there is sufficient voltage across the series pass
transistor for it to regulate correctly.) In this way the current sense resistor
will not cause any reduction in the voltage output from the power supply
regulator circuit.
The power supply current limiter circuit is shown within the
circuit of a very simple regulator. However it can be placed within most
regulator circuits made from discrete components with little change. For
regulator circuits using regulator integrated circuits, these are virtually
certain to include current limiter circuitry based around this principle.
|