Diode voltage multiplier
-a circuit using diodes that multiplies the incoming voltage
Within a power supply or other rectifier circuit it is
possible to configure the diodes in such a way that they double, triple or more,
the level of the incoming voltage. This type of voltage multiplier circuit finds
uses in many applications where a low current, high voltage source is required.
Although there are some variations on the basic circuit,
these ones shown below use a single winding on the transformer that is required,
one side of which can be grounded. Alternatively another AC source can be used.
In this configuration the circuit is particularly convenient as the AC source
does not need to be isolated from ground.
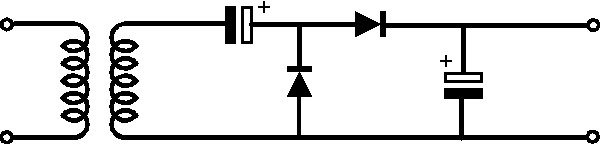
Diode voltage doubler circuit
In this voltage doubler circuit the first diode rectifies the
signal and its output is equal to the peak voltage from the transformer
rectified as a half wave rectifier. An AC signal via the capacitor also reaches
the second diode, and in view of the DC block provided by the capacitor this
causes the output from the second diode to sit on top of the first one. In this
way the output from the circuit is twice the peak voltage of the transformer,
less the diode drops.
Variations of the basic circuit and concept are available to
provide a voltage multiplier function of almost any factor. Applying the same
principle of sitting one rectifier on top of another and using capacitive
coupling enables a form of ladder network to built up.
The voltage multiplier circuits are very useful. However they
are normally suitable only for low current applications. As the voltage
multiplication increases the losses increase. The source resistance tends to
rise, and loading becomes an issue. For each diode in the chain there is the
usual diode drop (normally 0.6 volts for a silicon diode), but the reactance of
the capacitors can become significant, especially when mains frequencies of 50
or 60 Hz are used. High voltage high value capacitors can be expensive and
large. This may provide physical constraints for making them too large.
|