PIN diode attenuator
- a constant impedance attenuator design for radio frequency or RF
circuit design applications
Electronically controllable PIN diode attenuators are often used in radio
frequency or RF circuit designs. It is often necessary to be able to control the
level of a radio frequency signal using a control voltage. It is possible to
achieve this using a PIN diode attenuator circuit. Some circuits do not offer a
constant impedance, whereas this PIN diode attenuator gives a satisfactory
match.
The PIN diode variable attenuator is used to give attenuation over a range of
about 20 dB and can be used in 50 ohm systems. The inductor L1 along with the
capacitors C4 and C5 are included to prevent signal leakage from D1 to D2 that
would impair the performance of the circuit.
The maximum attenuation is achieved when Vin is at a minimum. At this point
current from the supply V+ turns the diodes D1 and D2 on effectively shorting
the signal to ground. D3 is then reverse biased. When Vin is increased the
diodes D1 and D2 become reverse biased, and D3 becomes forward biased, allowing
the signal to pass through the circuit.
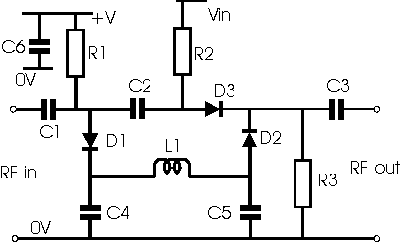
PIN diode variable attenuator
Typical values for the circuit might be: +V : 5 volts; Vin : 0 - 6 volts; D1
to D3 HP5082-3080 PIN diodes; R1 2k2; R2 : 1k; R3 2k7; L1 is self resonant above
the operating frequency, but sufficient to give isolation between the diodes D1
and D2.
These values are only a starting point for an experimental design, and are
only provided as such. The circuit may not be suitable in all instances.
Choice of diode
Although in theory any diode could be used in this position, PIN diodes have a
number of advantages as switches. In the first place they are more linear than
ordinary PN junction diodes. This means that in their action as a radio
frequency switch they do not create as many spurious products and additionally
as an attenuator they have a more useful curve. Secondly when reverse biased and
switched off, the depletion layer is wider than with an ordinary diode and this
provides for greater isolation when switching.
|