RDS - The Radio Data System
RDS or Radio Data System is standard on most car radios and hi-fi tuners
today. RDS is used on VHF FM radio broadcast transmissions and provides a number
of facilities that are of great use to all radio listeners, but particularly to
those radio listeners in cars. RDS enables traffic reports to be received more
easily, and provides many facilities including enabling the radio station name
to be displayed on the radio display.
The system has gained a considerable amount of popularity and is widely used
in Europe where it has been established for a number of years.
How RDS Works
RDS operates by adding data to the baseband signal that is used to modulate the
radio frequency carrier. The baseband signal consists of a number of components.
Firstly there is the mono audio consisting of the left plus right (L+R)
component that is transmitted at the normal audio frequencies up to 15 kHz. The
stereo difference signal is then amplitude modulated as a double sideband
suppressed carrier signal at 38 kHz. A pilot tone at 19 kHz (half the frequency
of the stereo difference signal subcarrier) is also transmitted and this is used
to enable the receiver demodulator to exactly recreate the 38 kHz subcarrier to
decode the stereo difference signal.
The stereo difference signal is above the audio hearing range and as a result
it does not detract from the normal mono signal. When adding anything new to a
transmission, compatibility must be maintained with existing radios.
The RDS information is placed above the stereo difference signal on a 57 kHz
subcarrier as shown. This happens to be three times the stereo pilot tone
frequency. For stereo transmissions the RDS subcarrier is locked onto the pilot
tone. It can either be in-phase with the third harmonic of the tone, or as in
the case of the BBC it can be in quadrature.
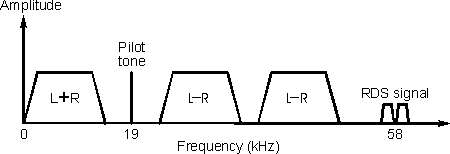
The structure of the baseband signal including the RDS
subcarrier
The actual subcarrier that is used to carry the information is phase
modulated to carry the data. It uses a form of modulation called Quadrature
Phase Shift Keying (QPSK). This gives good immunity to data errors caused by
noise whilst still allowing the data to be transmitted at a suitable rate.
Combined with the fact that the subcarrier operates at a harmonic of the pilot
tone, these facts minimise the possibility of interference to the audio signals.
Baseband Coding
The rate at which data is transmitted is 1187.5 bits per second. This is equal
to the frequency of the RDS subcarrier divided by 48. By adopting this data rate
the decoding circuits to operate synchronously. This reduces problems with
spurious signals in the decoding circuits.
Data is transmitted in groups consisting of four blocks. Each block contains
a 16 bit information word and a 10 bit check word as shown. This means that with
the data rate of 1187.5 bit per second approximately 11.4 groups can be
transmitted each second.
A 10 bit check word may seem to be long. However it is very important in view
of the poor signal conditions which can exist. This can be particularly true for
car or portable radios. The check word enables the radio decoder to detect and
correct errors. It also provides a method for synchronisation.
The data groups are structured so that data can be transmitted as efficiently
as possible. Different stations will want to transmit different types of data at
different times. To cater for this there are a there are a total of 16 different
group structures. Their applications are outlined in Figure 3.
Mixing of different types of data within groups is kept to a minimum. However
the coding structure is such that messages which need repeating most frequently
normally occupy the same position within groups. For example the first block in
a group always contains the PI code and PTY and TP are to be found in block 2.
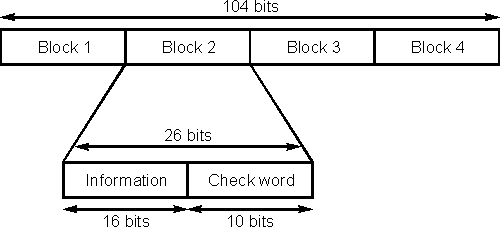
RDS data structure
In order that a radio knows how to decode the data correctly, each type of
group has to be identified. This function is performed by a four bit code
occupying the first four bits in the second block.
Once generated the data is coded onto the subcarrier in a differential
format. This allows the data to be decoded correctly whether the signal is
inverted or not. When the input data level is "0" the output remains unchanged
but when a "1" appears at the input the output changes its state.
With the basic signal generated the spectrum has to be carefully limited.
This has to be done to avoid any cross talk in phase locked loop decoders. The
power density close to 57 kHz is limited by the encoding each bit as a biphase
signal. In addition to this the coded data is passed through a low pass filter.
Facilities
The RDS system offers a wide range of very useful facilities. The most widely
publicised one is that of being able to provide travel news. This is available
on most local radio stations. All of these stations transmit the TP code to
identify that travel messages are flagged by RDS. When the radio is set for
travel news it will only tune to stations which carry the TP indication. As the
station is about to broadcast a travel announcement the TA code is transmitted.
If a CD or cassette is being played then most sets will actually pause the CD or
tape and then allow the travel announcement to be heard. In addition to this the
volume may also be set slightly higher to allow the announcement to be heard
more easily.
Autotuning
RDS brings intelligence into the tuning of a radio. The autotuning facility
comes into its own on long journeys when the car moves from the service area of
one transmitter to the next. Without RDS the radio has to be manually tuned to
the next station. This is not always easy because it is difficult to reliably
detect which is the strongest station.
An RDS set will look for the Programme Identification or PI code. A national
network will be broadcast from a large number of different transmitters around
the country. The station or network eg Radio 4 will have its own PI code. When
the radio moves out of the range of one transmitter the radio will seek the
strongest signal which has the same PI code, allowing the radio to remain tuned
to the same programme.
When radios fitted with RDS store a station frequency, they also store the PI
code along side it. This has the advantage that when the radio is turned on in a
place outside the coverage area for the transmitter frequency which is stored
then the radio will seek the strongest signal which has the correct PI code.
Local radio stations also have a PI code. In view of the local nature of
these stations the PI code works slightly differently.
If the station has two or more transmitters then the PI code will operate in
the normal way when it is range of these transmitters. However when the radio
moves outside this coverage area it will retune to the strongest signal of the
same type of station.
The PI code consists of four characters. The first indicates the country of
origin and for the UK this is C. The next one indicates the type of coverage.
The figure "2" indicates a national station, and the final two characters are
the programme reference. For example Radio 3 has the PI code C203 and BBC GLR
has C311.
Instant Tuning
It takes a number of seconds for the radio to search for the strongest signal
with the correct PI code. During this time the radio would mute itself and the
listener would have an annoying gap in listening. To enable the set to tune
itself very quickly from one transmission to the next each transmitter
broadcasts a short list of frequencies of adjacent transmitters. This vastly
reduces the amount of seeking which the radio set has to perform. In addition to
this a second front end is often employed to constantly detect the strength of
the alternative frequency transmissions. This results in much faster changes in
setting - to the extent that the listener should not be able to detect when the
radio changes from one transmitter to another.
Another facility associated with tuning is called the Programme Service Name
(PS). This enables the set to display the station name. This normally takes a
second or two to come up on the display after the station has been tuned in.
However it is a most useful facility with the ever-increasing number of stations
on the air
New Facilities
A new feature which has been added to RDS is called Enhanced Other Networks
(EON). This allows the set to listen to one station like a national network, but
still be interrupted by travel news from a local radio station. This feature
even allows announcements to be heard whilst travelling in silence or listening
to a tape.
EON requires a large amount of co-ordination between the different stations.
To achieve this, the BBC have a central computer specifically for this purpose.
When a local radio station is about to transmit a traffic message the fact is
flagged to the computer. In turn this directs the relevant national radio
transmitters to indicate this fact, thereby enabling the radios to change
frequency to the local radio station to receive the message. Once the message is
complete the radio will return to its original station.
EON is relatively new and the first sets to have it included only appeared in
1991. Although it is being introduced on more sets, the majority still does not
have it. However with manufacturers constantly bringing new sets onto the market
EON should be included on far more sets in a year or two.
Summary of RDS Abbreviations:-
| AF |
Alternative Frequencies |
A list of a station's frequencies in
adjacent transmitter areas. |
| CT |
Clock Time and Date |
Data containing time and date information
so that the receiver can display. Using this signal has the advantage
over a self-contained clock in the radio that it adjusts itself to
changes between BST and GMT (UTC) and it does not loose or gain time. |
| DI |
Decoder Information |
This signal allows for miscellaneous
function in the radio to be controlled |
| EON |
Enhanced Other Networks |
Information transmitted giving the radio a
cross-reference to other stations for Travel service and other features. |
| MS |
Music/Speech |
This allows for the relative levels of
speech and music to be altered. |
| PI |
Programme Identification |
This is a station code used in conjunction
with AF data to provide automatic tuning to the best signal for a chosen
service. |
| PIN |
Programme Identification Number |
This signal identifies a given programme
and allows the radio to turn itself (and possibly a recorder) on for
that programme. |
| PTY |
Programme Type Selection |
A signal which allows for the selection of
listening by one of 15 types of programme rather than by the station. |
| PS |
Programme Service Name |
A signal which enables the name of the
station to be displayed. |
| RT |
Radio Text |
This allows information about the programme
to be displayed by the radio. |
| TDC |
Transparent Data Channel |
This allows for data to downloaded via RDS. |
| TP/TA |
Travel Service |
These signals enable the travel information
to be heard, regardless of the choice of listening. |
|

