Radio receiver signal to noise ratio (SNR)
- an overview of the signal to noise (S/N) ratio or SNR used in determining
and specifying the sensitivity of radio receivers used alone of within radio
communications systems.
The noise performance and hence the signal to noise ratio is
a key parameter for any radio receiver. It is a measure of its sensitivity
performance and this is of prime importance in many applications from simple
broadcast receivers to those used in more professional applications such as
fixed or mobile radio communications, two way radio communications systems,
satellite radio and more.
There are a number of ways in which the noise performance,
and hence the sensitivity of a radio receiver can be measured. The most obvious
method is to compare the signal and noise levels for a known signal level, i.e.
the signal to noise (S/N) ratio or SNR. Obviously the greater the difference
between the signal and the unwanted noise, i.e. the greater the S/N ratio, the
better the radio receiver sensitivity performance.
As with any sensitivity measurement, the performance of the
overall radio receiver is determined by the performance of the front end RF
amplifier stage. Any noise introduced by the first RF amplifier will be added to
the signal and amplified by subsequent amplifiers in the receiver. As the noise
introduced by the first RF amplifier will be amplified the most, this RF
amplifier becomes the most critical in terms of radio receiver sensitivity
performance. Thus the first amplifier of any radio receiver should be a low
noise amplifier.
Methods of measuring radio receiver sensitivity
Although there are many ways of measuring the sensitivity
performance of a radio receiver, the S/N ratio or SNR is one of the most
straightforward and it is used in a variety of applications. However it has a
number of limitations, and although it is widely used, other methods including
noise figure are often used as well. Nevertheless the S/N ratio or SNR is an
important specification, and it will be seen in many radio receiver
specification sheets.
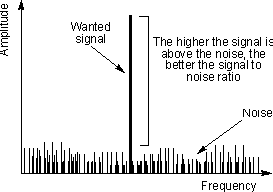
Signal to noise ratio for a radio receiver
The difference is normally shown as a ratio between the
signal and the noise (S/N) and it is normally expressed in decibels. As the
signal input level obviously has an effect on this ratio, the input signal level
must be given. This is usually expressed in microvolts. Typically a certain
input level required to give a 10 dB signal to noise ratio is specified.
Effect of radio receiver bandwidth
A number of other factors apart from the basic performance of
the set can affect the SNR specification. The first is the actual bandwidth of
the receiver. As the noise spreads out over all frequencies it is found that the
wider the bandwidth of the receiver, the greater the level of the noise.
Accordingly the receiver bandwidth needs to be stated.
Additionally it is found that when using AM the level of
modulation has an effect. The greater the level of modulation, the higher the
audio output from the receiver. When measuring the noise performance the audio
output from the receiver is measured and accordingly the modulation level of the
AM has an effect. Usually a modulation level of 30% is chosen for this
measurement.
Typical figures
This method of measuring the performance is most commonly
used for HF communications receivers. Typically one might expect to see a figure
in the region of 0.5 microvolts for a 10 dB S/N in a 3 kHz bandwidth for SSB or
Morse. For AM a figure of 1.5 microvolts for a 10 dB S/N in a 6 kHz bandwidth at
30% modulation for AM might be seen.
Points to note when measuring SNR
SNR is a very convenient method of quantifying the
sensitivity of a receiver, but there are some points to note when measuring and
interpreting the figures. To investigate these it is necessary to look at the
way the measurements of SNR are made. A calibrated RF signal generator is used
as a signal source for the receiver. It must have an accurate method of setting
the output level down to very low signal levels. Then at the output of the
receiver a true RMS AC voltmeter is used to measure the output level.
- S/N and (S+N)/N With the generator signal switched off a
50 Ohm match is given to the receiver and the audio meter will detect the
noise generated by the receiver itself. This level is noted and the signal
turned on. Its level is adjusted until the audio level meter reads a level
which is 10 dB higher than just the noise on its own. The level of the
generator is that required to give the 10 dB signal to noise ratio.
The last statement was not strictly true. Whilst the first reading of the
noise is quite accurate, the second reading of the signal also includes some
noise as well. In view of this many manufacturers will specify a slightly
different ratio: namely signal plus noise to noise (S+N/N). In practice the
difference is not particularly large, but the S+N/N ratio is more correct.
- PD and EMF Occasionally the signal generator level in
the specification will mention that it is either PD or EMF. This is actually
very important because there is a factor of 2:1 between the two levels. For
example 1 microvolt EMF. and 0.5 microvolt PD are the same. The EMF
(electro-motive force) is the open circuit voltage, whereas the PD
(potential difference) is measured when the generator is loaded. As a result
of the way in which the generator level circuitry works it assumes that a
correct (50 Ohm) load has been applied. If the load is not this value then
there will be an error. Despite this most equipment will assume values in PD
unless otherwise stated.
Summary
While there are many parameters that are used for specifying
the sensitivity performance of radio receivers, the signal to noise ratio is one
of the most basic and easy to comprehend. It is therefore widely used for many
radio receivers used in applications ranging from broadcast reception to fixed
or mobile radio communications.
|

