SINAD and SINAD measurements for radio receivers
- an overview or tutorial of the basics of the SINAD measurement and how
SINAD may be used in specifying the sensitivity performance of many radio
receivers and radio communications systems.
One of the measurements that can be made to assess and
specify the sensitivity performance of a radio receiver is SINAD. It is very
useful in many applications including many two way radio communications systems,
mobile radio communications systems, and particularly those at VHF and above.
While SINAD may not used as widely as the signal to noise
ratio, or noise figure it is nevertheless used commonly and can be found in the
specifications of many radio receivers used in fixed and mobile radio
communications systems.. SINAD is often used in conjunction with FM receivers,
but it can also be used for AM and SSB quite easily.
As with any radio receiver, the design of the RF amplifier is
key to its sensitivity performance. A poorly performing RF amplifier will
degrade the performance of the whole radio receiver. However a high performance
low noise RF amplifier will enable the overall set to provide a high level of
sensitivity. Accordingly time should be focussed in the design of the RF
amplifier in order that it should reach the required level of performance.
What is SINAD?
SINAD is a measurement that can be used for any radio
communication device to look at the degradation of the signal by unwanted or
extraneous signals including noise and distortion. However the SINAD measurement
is most widely used for measuring and specifying the sensitivity of a radio
receiver.
The actual definition of SINAD is quite straightforward. It
can be summarised as the ratio of the total signal power level (Signal + Noise +
Distortion) to unwanted signal power (Noise + Distortion). Accordingly, the
higher the figure for SINAD, the better the quality of the audio signal.
The SINAD figure is expressed in decibels (dB) and can be
determined from the simple formula:
SINAD = 10Log ( SND / ND )
where:
SND = combined Signal + Noise + Distortion power level
ND = combined Noise + Distortion power level
It is worth noting that SINAD is a power ratio and not a
voltage ratio for this calculation.
Making SINAD measurements
To make the measurement a signal modulated with an audio tone
is entered into the radio receiver. A frequency of 1 kHz is taken as the
standard as it falls in the middle of the audio bandwidth. A measurement of the
whole signal, i.e. the signal plus noise plus distortion is made. As the
frequency of the tone is known, the regenerated audio is passed through a notch
filter to remove the tone. The remaining noise and distortion is then measured.
Although it is most common to measure the electrical output
at the radio receiver audio output terminals, another approach that is not as
widely used, is to pass the signal into the loudspeaker and then use a
transducer connected to SINAD meter to convert the audio back into an electrical
signal. This will ensure that any distortion included by the speaker is
incorporated, and it may overcome problems with gaining access to the speaker
connections in certain circumstances where this may not be possible.
Obtaining the figures for the signal plus noise plus
distortion and the noise plus distortion it is then possible to calculate the
value of SINAD for the radio receiver of other piece of equipment.
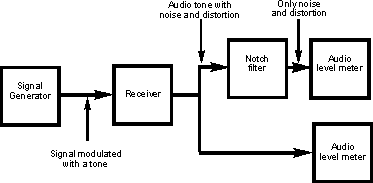
The set up used for making SINAD measurements
While the measurements for SINAD can be made using individual
items of test equipment, a number of SINAD meters are made commercially. These
SINAD meters incorporate all the required circuitry and can be connected
directly to radio receivers to make the measurements. Accordingly SINAD meters
are a particularly convenient method of making these measurements.
Filter for SINAD measurements
The notch filter that is required for SINAD measurements to
be made has an effect on the measurement. In an ideal world the filter would be
infinitely sharp a notch out only the modulating tone. However in the real world
the filter will have a finite bandwidth. As its bandwidth increases, so it will
remove noise and distortion as well as the tone. However as the distortion
products will typically result from the second and third harmonics of the tone,
the filter will not have an effect on this element of the reading. Nevertheless
it may still have an effect on the noise levels.
In view of this problem some standards set down
specifications or guidelines for the filter used in the SINAD measurement. ETSI
(European Telecommunications Standards Institute) defines a notch filter (ETR
027). With the standard tone frequency of 1 kHz, it states that a filter used
for SINAD measurements shall be such that the output the 1000 Hz tone shall be
attenuated by at least 40 dB and at 2000 Hz the attenuation shall not exceed 0.6
dB. The filter characteristic shall be flat within 0.6 dB over the ranges 20 Hz
to 500 Hz and 2000 Hz to 4000 Hz. In the absence of modulation the filter shall
not cause more than 1 dB attenuation of the total noise power of the audio
frequency output of the receiver under test.
In addition to the filter performance another critical area
of a SINAD measurement is the measurement of the output signal power levels.
These have to be a true power measurements that accommodate the different form
factors of the variety of waveforms, i.e. sine wave for the 1 kHz tone and its
harmonics, but the noise will be random and have a different form factor.
Applications of SINAD measurements
SINAD measurements give an assessment of the signal quality
from a receiver under a number of conditions. As such SINAD measurements can be
used for assessing a number of elements of receiver performance.
Receiver sensitivity: The most common use of
the SINAD measurement is to assess the sensitivity performance of a radio
receiver. To achieve this the sensitivity can be assessed by determining the RF
input level at the antenna that is required to achieve a given figure of SINAD.
Normally a SINAD value of 12 dB is taken as this corresponds to a distortion
factor of 25%, and a modulating tone of 1 kHz is used. It is also necessary to
determine other conditions. For AM it is necessary to specify the depth of
modulation and for FM the level of deviation is required. For FM analogue
systems ETSI specifies the use of a deviation level of 12.5% of the channel
spacing
A typical specification might be that a receiver has a
sensitivity of 0.25 uV [microvolts] for a 12 dB SINAD. Obviously the lower the
input voltage needed to achieve the given level of SINAD, the better the
receiver performance.
Adjacent channel rejection: This parameter is
a measure of the ability of the receiver to reject signals on a nearby channel.
As the adjacent channel performance degrades, so the levels of noise and
extraneous signals will increase, thereby degrading the SINAD performance.
An initial measurement of SINAD is made at a given level and
this is known as the reference sensitivity. The RF input level of the signal for
the SINAD measurement is then increased by 3 dB at the receiver antenna input. A
second source or signal with modulated with a 400 Hz tone is added with its
frequency set to an adjacent channel or at a specific offset from the carrier
source used for the basic SINAD measurement. It will be found that the
interferer will cause the 400 Hz tone to appear in the audio of the receiver as
its level is increased. This will be seen as a degradation in the SINAD as the
400 Hz tone will pass through the SINAD meter notch filter.
With the measurement system set up, the interferer signal
level is raised until the SINAD value is degraded to the original value obtained
at the reference sensitivity. Then the ratio of the interfering level to the
wanted signal is the adjacent channel rejection.
Receiver blocking: SINAD can be used to form
the basis of a receiver blocking measurement. As with other similar measurements
a reference SINAD sensitivity level is found. The level of the SINAD signal is
increased by 3 dB at the antenna. An un-modulated off channel signal is then
added and its level raised until the receiver desensitises to an extent whereby
the reference SINAD level is reached.
Summary
SINAD is a particularly useful measurement format that can be
used to determine the performance of a radio receiver under a variety of
conditions. Although SINAD is primarily used to specify the basic sensitivity
performance of many radio receivers, it can be used for other parameters as
well. Additionally it is chiefly used for FM systems, but its use is equally
applicable to AM and SSB, and it finds applications for many fixed or mobile
radio communications systems including two way radio communications links. It
may also be used for digital radio systems as well, although this is not common
practice as a measurement known as bit error rate (BER) is more widely used.
The overall figure for SINAD will be chiefly dependent upon
the performance of the RF amplifier in the receiver. A low noise RF amplifier
will enable the set as a whole to provide a good SINAD performance.
|

