Reflection, refraction and diffraction of radio signals
- a summary, tutorial or overview of the basics of electromagnetic waves and
the electromagnetic spectrum, looking particularly at radio waves and their
propagation..
Reflection, refraction and diffraction of radio signals are at
the very core of radio signal propagation, and radio technology as a whole.
While the mathematics behind electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic
spectrum can become particularly complicated, it is not necessary to have to
deal with this branch of science everyday. However it is always useful to be
able to have a working knowledge.
Electromagnetic wave basics
Radio signals exist as a form of electromagnetic wave. These
radio signals are the same form of radiation as light, ultra-violet, infra-red,
etc., differing only in the wavelength or frequency of the radiation.
Electromagnetic waves have two elements. They are made from
electric and magnetic components that are inseparable. The planes of the fields
are at right angles to each other and to the direction in which the wave is
travelling.
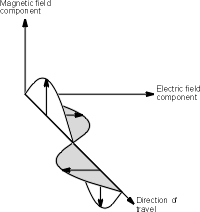
An electromagnetic wave
It is useful to see where the different elements of the wave
emanate from to gain a more complete understanding of electromagnetic waves. The
electric component of the wave results from the voltage changes that occur as
the antenna element is excited by the alternating waveform. The lines of force
in the electric field run along the same axis as the antenna, but spreading out
as they move away from it. This electric field is measured in terms of the
change of potential over a given distance, e.g. volts per metre, and this is
known as the field strength. This measure is often used in measuring the
intensity of an electromagnetic wave at a particular point. The other component,
namely the magnetic field is at right angles to the electric field and hence it
is at right angles to the plane of the antenna. It is generated as a result of
the current flow in the antenna.
Like other forms of electromagnetic wave, radio signals can
be reflected, refracted and undergo diffraction. In fact some of the first
experiments with radio waves proved these facts, and they were used to establish
a link between radio waves and light rays.
Wavelength, frequency and velocity
There are a number of basic properties of electromagnetic
waves, or any repetitive waves for that matter that are particularly important.
One of the first that is quoted is their speed. Radio waves
travel at the same speed as light. For most practical purposes the speed is
taken to be 300 000 000 metres per second although a more exact value is 299 792
500 metres per second. Although exceedingly fast, they still take a finite time
to travel over a given distance. With modern radio techniques, the time for a
signal to propagate over a certain distance needs to be taken into account.
Radar for example uses the fact that signals take a certain time to travel to
determine the distance of a target. Other applications such as mobile phones
also need to take account of the time taken for signals to travel to ensure that
the critical timings in the system are not disrupted and that signals do not
overlap.
Another major element of a radio wave is its wavelength. This
is the distance between a given point on one cycle and the same point on the
next cycle as shown. The easiest points to choose are the peaks as these are the
easiest to locate. The wavelength was used in the early days of radio
communications or wireless to determine the position of a signal on the dial of
a set. Although it is not used for this purpose today, it is nevertheless an
important feature of any radio signal or for that matter any electromagnetic
wave. The position of a signal on the dial of a radio set or its position within
the radio spectrum is now determined by its frequency as this provides a more
accurate and convenient method for determining the properties of the signal.
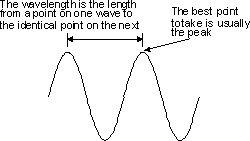
Wavelength of an electromagnetic wave
Finally the frequency of an radio signal or electromagnetic
wave is of great importance. This is the number of times a particular point on
the wave moves up and down in a given time (normally a second). The unit of
frequency is the Hertz and it is equal to one cycle per second. This unit is
named after the German scientist who discovered radio waves. The frequencies
used in radio are usually very high. Accordingly the prefixes kilo, Mega, and
Giga are often seen. 1 kHz is 1000 Hz, 1 MHz is a million Hertz, and 1 GHz is a
thousand million Hertz i.e. 1000 MHz. Originally the unit of frequency was not
given a name and cycles per second (c/s) were used. Some older books may show
these units together with their prefixes: kc/s; Mc/s etc. for higher
frequencies.
Frequency to Wavelength Conversion
Although wavelength was used as a measure for signals,
frequencies are used exclusively today. It is very easy to relate the frequency
and wavelength as they are linked by the speed of light as shown:
lambda = c / f
where lambda = the wavelength in metres
f = frequency in Hertz
c = speed of radio waves (light) taken as 300 000 000 metres per second for all
practical purposes.
Electromagnetic spectrum and the radio spectrum
Electromagnetic waves have an enormous range, and as a result
it is very convenient to see where each of the different forms of radiations
fits within the spectrum as a whole. It can be seen that radio signals have the
lowest frequency, and hence the longest wavelengths. Above the radio spectrum,
other forms of radiation can be found. These include infra red radiation, light,
ultraviolet and a number of other forms of radiation.
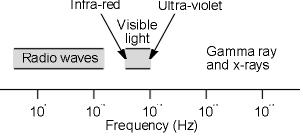
The electromagnetic spectrum
Even within the radio spectrum there is an enormous range of
frequencies. It extends over many decades. In order to be able to categorise the
different areas and to split the spectrum down into more manageable sizes, the
spectrum is split into different segments.
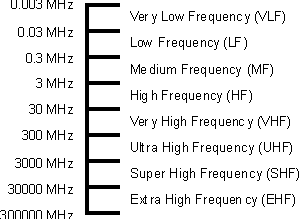
The spectrum of electromagnetic waves
Summary
Electromagnetic waves, and in this instance, radio waves, are
affected by the media through which they travel. The degree to which they are
affected, and the way in which they are affected, often depends upon the
frequency. Signals can be reflected, refracted, and diffracted, altering their
paths. At other times signals may be absorbed, reducing the distances over which
they may travel. However many signals may travel for light years, as in the case
of signals travelling from stars. However, for most of us the distances that can
be reached by a Wi-Fi or cellular telephone may be of more interest.
|

