| Circuit Analysis Technique |
Circuit Analysis Techniques
Ohm's Law states the voltage across a resistor,
R (or impedance, Z) is directly proportional to the current
passing through it (the resistance/impedance is the proportionality constant)

Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL): the algebraic sum of
the voltages around any loop of N elements is zero (like pressure drops
through a closed pipe loop)
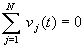
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL): the algebraic sum of
the currents entering any node is zero, i.e., sum of currents entering
equals sum of currents leaving (like mass flow at a junction in a pipe)
Nodal analysis is generally best in the case of several voltage sources. In
nodal analysis, the variables (unknowns) are the "node voltages."
Nodal Analysis Procedure:
- Label the N node voltages. The node voltages are defined positive
with respect to a common point (i.e., the reference node) in the
circuit generally designated as the ground (V = 0).
- Apply
KCL at each node in terms of node voltages.
- Use KCL to write a current balance at N-1 of the N
nodes of the circuit using assumed current directions, as necessary.
This will create N-1 linearly independent equations.
- Take advantage of supernodes, which create constraint
equations. For circuits containing independent voltage sources, a
supernode is generally used when two nodes of interest are separated by
a voltage source instead of a resistor or current source. Since the
current (i) is unknown through the voltage source, this extra
constraint equation is needed.
- Compute the currents based on voltage differences between nodes.
Each resistive element in the circuit is connected between two nodes;
the current in this branch is obtained via
Ohm's Law where Vm is the positive side and
current flows from node m to n (that is, I is m
--> n).

- Determine the unknown node voltages; that is, solve the N-1
simultaneous equations for the unknowns, for example using Gaussian
elimination or matrix solution methods.
Nodal Analysis Example
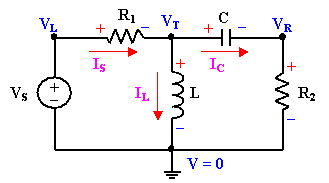 |
- Label the nodal voltages.
- Apply KCL.
- KCL at top node gives IS = IL + IC
- Supernode constraint eq. of VL = VS
-
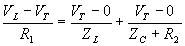
- Solve for VT for instance.
|
Mesh (loop) analysis is generally best in the case of several current
sources. In loop analysis, the unknowns are the loop currents. Mesh analysis
means that we choose loops that have no loops inside them.
Loop Analysis Procedure:
- Label each of the loop/mesh currents.
- Apply
KVL to loops/meshes to form equations with current variables.
- For N independent loops, we may write N total
equations using KVL around each loop. Loop currents are those
currents flowing in a loop; they are used to define branch currents.
- Current sources provide constraint equations.
- Solve the equations to determine the user defined loop currents.
Mesh Analysis Example:
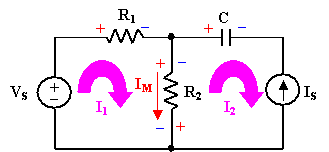 |
- Label mesh currents.
- Apply KVL.
- Left loop KVL:
- VS = R1I1 + R2(I1-I2)
- Constraint equation I2 = -IS.
- Solve for I1 and I2. Note: Branch current
from mesh currents: IM = I1 - I2
|
In any linear circuit containing multiple independent sources, the
current or voltage at any point in the network may be calculated as the
algebraic sum of the individual contributions of each source acting alone.
Procedure:
- For each independent voltage and current source (repeat the following):
- Replace the other independent voltage sources with a short
circuit (i.e., v = 0).
- Replace the other independent current sources with an open
circuit (i.e., i = 0).
- Note: Dependent sources are not changed!
- Calculate the contribution of this particular voltage or current
source to the desired output parameter.
- Algebraically sum the individual contributions (current and/or voltage)
from each independent source.
An ac voltage source V in series with an impedance Z can be
replaced with an ac current source of value I=V/Z in
parallel with the impedance Z.
An ac current source I in parallel with an impedance Z can be
replaced with an ac voltage source of value V=IZ in series with
the impedance Z.
Likewise, a dc voltage source V in series with a resistor R can
be replaced with a dc current source of value i = v/R in
parallel with the resistor R; and vice versa.
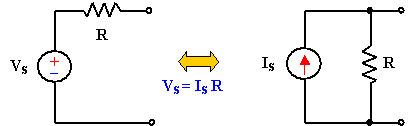
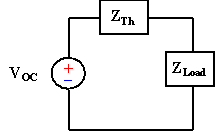
Th�venin's Theorem states that we can replace entire network,
exclusive of the load, by an equivalent circuit that contains only an
independent voltage source in series with an impedance (resistance) such that
the current-voltage relationship at the load is unchanged.
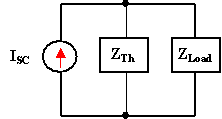
Norton's Thereom is identical to Th�venin's Theorem except that the
equivalent circuit is an independent current source in parallel with an
impedance (resistor). Hence, the Norton equivalent circuit is a
source
transformation of the Th�venin equivalent circuit.
| Th�venin Equivalent Circuit |
Norton Equivalent Circuit |
 |
 |
Procedure:
- Pick a good breaking point in the circuit (cannot split a dependent
source and its control variable).
- Thevenin: Compute the open circuit voltage, VOC.
Norton: Compute the short circuit current, ISC.
- Compute the Thevenin equivalent resistance, RTh (or
impedance, ZTh).
- If there are only independent sources, then short circuit all the
voltage sources and open circuit the current sources (just like
superposition).
- If there are only dependent sources, then must use a test voltage or
current source in order to calculate RTh= vTest/iTest
(or ZTh=VTest/ITest).
- If there are both independent and dependent sources, then compute
RTh (or ZTh) from RTh=
vOC/iSC (or ZTh=VOC/ISC).
- Replace circuit with Thevenin/Norton equivalent.
Thevenin: VOC in series with RTh
(or ZTh).
Norton: ISC in parallel with RTh
(or ZTh).
- Note: for 3(b) the equivalent network is merely RTh
(or ZTh), that is, no current or voltage sources.
|

