Cell Division
Cells divide when an animal grows, when its body repairs an injury and when
it produces sperm and eggs (or ova). There are two types of cell division:
Mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis. This is the cell division that occurs when an animal grows
and when tissues are repaired or replaced. It produces two new cells (daughter
cells) each with a full set of chromosomes that are identical to each other and
to the parent cell. All the cells of an animal�s body therefore contain
identical DNA.
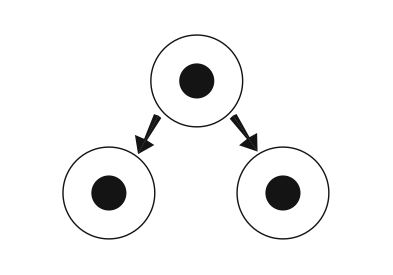
Diagram 3.16 - Division by mitosis results in 2 new cells identical to each
other and to parent cell.
Meiosis. This is the cell division that produces the ova and sperm
necessary for sexual reproduction. It only occurs in the ovary and testis.
The most important function of meiosis it to halve the number of chromosomes
so that when the sperm fertilises the ovum the normal number is regained. Body
cells with the full set of chromosomes are called diploid cells, while
gametes (sperm and ova) with half the chromosomes are called haploid
cells.
Meiosis is a more complex process than mitosis as it involves two divisions
one after the other and the four cells produced are all genetically different
from each other and from the parent cell.
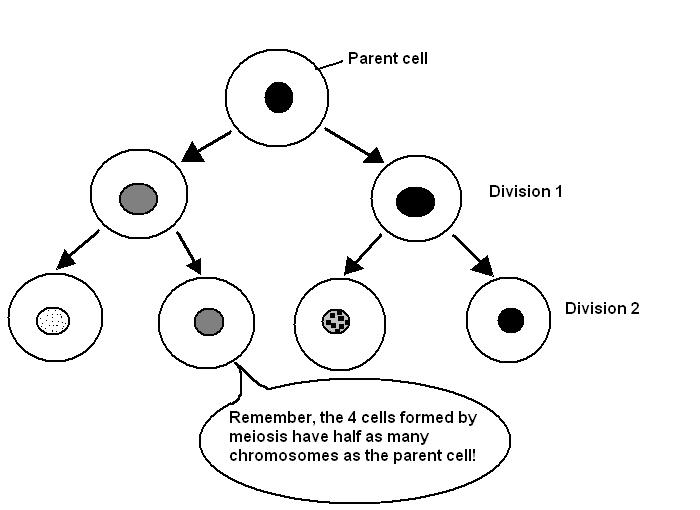
Diagram 3.17 - Division by meiosis results in 4 new cells that are genetically
different to each other.
This fact that the cells formed by meiosis are all genetically different from
each other and from the parent cell can be seen in litters of kittens where all
the members of the litter are different from each other as well as being
different from the parents although they display characteristics of both.
The Cell As A Factory
To make the function of the parts of the cell easier to understand and
remember you can compare them to a factory. For example:
- The nucleus (1) is the managing director of the factory consulting the
blueprint (the chromosomes) (2);
- The mitochondria (3) supply the power
- The ribosomes (4) make the products;
- The chloroplasts of plant cells (5) supply the fuel (food)
- The Golgi apparatus (6) packages the products ready for dispatch;
- The ER (7) modifies, stores and transports the products around the
factory;
- The plasma membrane is the factory wall and the gates (8);
- The lysosomes dispose of the waste and worn-out machinery.
Summary
- Cells consist of three parts: the plasma membrane, cytoplasm and
nucleus.
- Substances pass through the plasma membrane by diffusion (gases,
lipids), osmosis (water), active transport (glucose, ions),
phagocytosis (particles), pinocytosis (fluids) and exocytosis
(particles and fluids).
- Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a
semipermeable membrane. Water diffuses from high water "concentration"
to low water "concentration".
- The cytoplasm consists of cytosol in which are suspended cell
inclusions and organelles.
- organelles include ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria,
Golgi bodies and lysosomes.
- The nucleus controls the activity of the cell. It contains the
chromosomes that are composed of DNA.
- The cell divides by mitosis and meiosis
|