Theorems Introduction
From our earlier chapter we know
that, in statistical experiments, if the events A and B are independent,
then
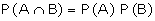
But suppose the two events are not
independent, that is the occurrence of one depends on the occurrence of
other, then how do we compute
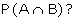 This can be explained by conditional probability.
This can be explained by conditional probability.
Baye's theorem is named after the
British mathematician Thomas Bayes who published it in a research paper
in 1763. It gives one of the important applications of the conditional
probabilities by using the additional information supplied by the
experiment or the past records.
|