|
Mechanisms can be divided into planar mechanisms and
spatial mechanisms, according to the relative motion of the rigid
bodies. In a planar mechanisms, all of the relative motions of the
rigid bodies are in one plane or in parallel planes. If there is any relative
motion that is not in the same plane or in parallel planes, the mechanism is
called the spatial mechanism. In other words, planar mechanisms
are essentially two dimensional while spatial mechanisms are three
dimensional. This tutorial only covers planar mechanisms.
Kinematics of mechanisms is concerned with the motion of the
parts without considering how the influencing factors (force and mass) affect
the motion. Therefore, kinematics deals with the fundamental concepts of space
and time and the quantities velocity and acceleration derived there from.
Kinetics deals with action of forces on bodies. This is where
the the effects of gravity come into play.
Dynamics is the combination of kinematics and
kinetics.
Dynamics of mechanisms concerns the forces that act on the
parts -- both balanced and unbalanced forces, taking into account the masses and
accelerations of the parts as well as the external forces.
A link is defined as a rigid body having two or more pairing
elements which connect it to other bodies for the purpose of transmitting force
or motion
(Ham et al. 58).
In every machine, at least one link either occupies a fixed position relative
to the earth or carries the machine as a whole along with it during motion. This
link is the frame of the machine and is called the fixed link.
The combination of links and pairs without a fixed link is not a mechanism
but a kinematic chain.
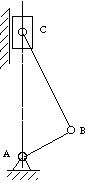
Figure 3-1 Skeleton outline
For the purpose of kinematic analysis, a mechanism may be represented in an
abbreviated, or skeleton, form called the skeleton outline of the
mechanism. The skeleton outline gives all the geometrical information necessary
for determining the relative motions of the links. In Figure 3-1, the skeleton
outline has been drawn for the engine shown in
Figure 2-1. This skeleton contains all necessary information to determine
the relative motions of the main links, namely, the length AB of the crank; the
length BC of the connecting rod; A the location of the axis of the main bearing;
and the path AC of point C, which represents the wrist-pin axis.
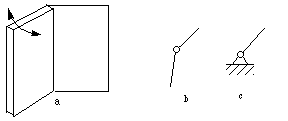
A pair is a joint between the surfaces of two rigid bodies that
keeps them in contact and relatively movable. For example, in
Figure 3-2, a door jointed to the frame with hinges makes revolute
joint (pin joint), allowing the door to be turned around
its axis. Figure 3-2b and c show skeletons of a revolute joint. Figure 3-2b is
used when both links joined by the pair can turn. Figure 3-2c is used when one
of the link jointed by the pair is the
frame.
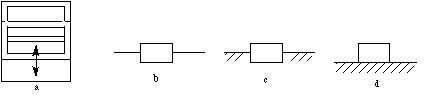
In
Figure 3-3a a sash window can be translated relative to the sash. This kind
of relative motion is called a prismatic pair. Its skeleton
outlines are shown in b, c and d. c and d are
used when one of the links is the
frame.
Generally, there are two kinds of pairs in mechanisms, lower
pairs and higher pairs. What differentiates them is the
type of contact between the two bodies of the pair. Surface-contact pairs are
called lower pairs. In
planar (2D) mechanisms, there are two subcategories of lower pairs --
revolute pairs and prismatic pairs, as shown in Figures
3-2 and
3-3, respectively. Point-, line-, or curve-contact pairs are called
higher pairs. Figure 3-4 shows some examples of higher pairs
Mechanisms composed of rigid bodies and lower pairs are called linkages.
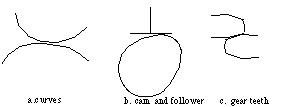
In kinematic analysis, a particular given mechanism is
investigated based on the mechanism geometry plus other known characteristics
(such as input angular velocity, angular acceleration, etc.).
Kinematic synthesis, on the other hand, is the process of designing a
mechanism to accomplish a desired task. Here, both choosing the types as well as
the dimensions of the new mechanism can be part of kinematic synthesis.
(Sandor & Erdman 84)
|

