Chemotherapy,
or the use of chemical agents to destroy cancer cells, is a mainstay in the
treatment of malignancies. The possible role in treating illness was
discovered when the bone marrow suppressive effect of nitrogen mustard was
noted in the early 1900's. Since that time, the search for drugs with
anticancer activity has continued, and the goal of treatment with
chemotherapy has evolved from relief of symptoms to cure. A major advantage
of chemotherapy is its ability to treat widespread or metastatic cancer,
whereas surgery and radiation therapies are limited to treating cancers that
are confined to specific areas.
Principles of Treatment
An understanding of the normal cell cycle and the behavior of malignant
or cancerous cells is necessary in order to comprehend how chemotherapy
destroys cancer cells. Below is an example of the cell cycle.
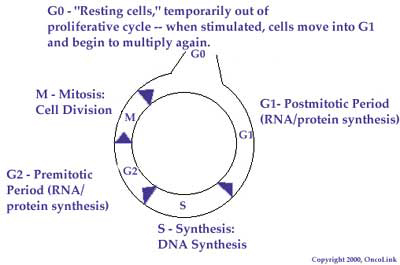
Chemotherapeutic Agents
Almost all chemotherapy agents currently available kill cancer cells by
affecting DNA synthesis or function, a process that occurs through the cell
cycle. Each drug varies in the way this occurs within the cell cycle.
The major categories of chemotherapy agents are alkylating agents,
antimetabolites, plant alkaloids, antitumor antibiotics, and steroid
hormones. Each drug is categorized according to their effect on the cell
cycle and cell chemistry.
- Alkylating agents kill cells by
directly attacking DNA. Alkylating agents may be used in the treatment
of chronic leukemias, Hodgkin's disease, lymphomas, and certain
carcinomas of the lung, breast, prostate and ovary.
Cyclophosphamide is an example of a commonly used alkylating agent.
- Nitrosoureas act similarly to
akylating agents and also inhibit changes necessary for DNA repair.
These agents cross the blood-brain barrier and are therefore used to
treat brain tumors, lymphomas, multiple myeloma, and malignant melanoma.
Carmustine
(BCNU) and
lomustine
(CCNU) are the major drugs in this category.
- Antimetabolites are that drugs
block cell growth by interfering with certain activities, usually DNA
synthesis. Once ingested into the cell they halt normal development and
reproduction. All drugs in this category affect the cell during the "S"
phase of the cell cycle. Antimetabolites may be used in the treatment of
acute and chronic leukemias, choriocarcinoma, and some tumors of the
gastrointestinal tract, breast and ovary. . Examples of commonly used
antimetabolites are
6-mercaptopurine and 5-fluorouracil (5FU).
- Antitumor antibiotics are a diverse
group of compounds. In general, they act by binding with DNA and
preventing RNA synthesis. These agents are widely used in the treatment
of a variety of cancers. The most commonly used drugs in this group are
doxorubicin (Adriamycin),
mitomycin-C, and
bleomycin.
- Plant (vinca) alkaloids are anti-tumor
agents derived from plants. These drugs act specifically by blocking
cell division during mitosisThey are commonly used in the treatment of
acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas,
neuroblastomas, Wilms' tumor, and cancers of the lung, breast and
testes.
Vincristine and
vinblastine are commonly used agents in this group.
- Steroid hormones are useful in
treating some types of tumors. This class includes
adrenocorticosteroids, estrogens, antiestrogens, progesterones, and
androgens. Although their specific mechanism of action is not clear,
steroid hormones modify the growth of certain hormone-dependent cancers.
Tamoxifen is an example, which is used for estrogen dependent breast
cancer.
In addition, other miscellaneous antineoplastic drugs exist whose
mechanisms of action do not permit broad categorization
Chemotherapy Administration
The most common routes of administration for chemotherapy are by mouth,
through a vein, and into a muscle. More recently, other methods have been
used to increase the local concentration of chemotherapy at the tumor site.
Chemotherapy can be administered directly into a specific cavity (intracavitary),
the abdomen (intraperitoneal), the lung (intrapleural), the central nervous
system (intra-thecal), or applied directly to the skin (topical).
Because many chemotherapeutic agents also effect healthy cells and
organs, the patient's laboratory data should be checked before chemotherapy
administration, including white blood cell count, hemoglobin/hematocrit,
platelet count, renal function tests, liver function tests. In addition,
assessment for organ specific drug effects will be performed on a periodic
basis. Abnormalities in any of these values may require dose adjustments or
the delay of therapy. Additionally, pretreatment actions, such as increased
fluids or administration of anti-nausea medicines may be needed to decrease
side effects.
Several strategies may be used to maximize the toxic effect of
chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is generally spaced out over an extended period
of time to gradually lower the number of tumor cells to the point where the
body's own immune responses can control further tumor growth. Many patients
receive their chemotherapy over a 4 to 12 month period of time.
Additionally, the interval between doses of chemotherapy is based on
achieving the greatest effect on the cancer cells, while also allowing the
healing of the normal healthy cells. Most often, patients receive their
chemotherapy every 3 to 4 weeks.
Strategies of Chemotherapy Administration
Combination Chemotherapy combines agents that differ in both the way they
act and their
side
effects. This is done to achieve maximum tumor effect with minimal side
effects. Because tumor cells have different biological characteristics
(heterogeneity), combining drugs may effectively eliminate cancer cells'
resistance to a single agent.
Adjuvant Chemotherapy may be given when no clear
evidence of cancer can be found, but certain factors (e.g. metastasis to the
lymph nodes) predict an increased risk of cancer recurrence. Use of
chemotherapy at an earlier stage of tumor growth may hinder the development
of resistance to chemotherapy often observed in large or metastatic cancers.
Combined Modality Chemotherapy may also be used in combination
with other treatment modalities, such as radiation or surgery. Therapies are
combined to obtain a greater response rate than could be achieved with a
single treatment modality. Today, using more than one treatment modality
effectively treats most cancers.
Hormonal Manipulation does not directly kill cells and, therefore,
is not curative. Their purpose is to prevent cell division and further
growth of hormone-dependent tumors. Their use is frequently reserved for the
management of patients with locally advanced or metastatic cancer.
Investigational Therapy
The identification and development of effective new anticancer drugs is
an on-going process. Following rigorous testing in laboratory animals and
experimental model systems, chemotherapy agents with demonstrated antitumor
activity are evaluated in clinical trials. In Phase I trials, the initial
phase of clinical investigation, a new treatment is evaluated in cancer
patients for the first time. The purpose of these studies is to determine
the associated side effects, the highest dose safely tolerated, and the
optimal schedule or mode of delivery of a new therapy. Phase II trials test
a new therapy (using the dose, method of administration, and schedule
defined in Phase I) in patients with a variety of tumors to determine
whether there is identifiable antitumor activity. In Phase III trials, new
therapies that exhibited activity in Phase II are compared to the standard
or best available therapy for each type of tumor tested.
Participation in a clinical trial is one treatment option, which may be
offered to patients at some point during therapy. The continuing progress of
cancer treatment depends upon the participation of adequate numbers of
patients in such studies.

