BASIC PHARMACOLOGY
HENDERSON-HESSELBACH EQUATION:
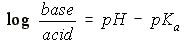
- Weak Acid
- pKa:
- If its pKa < pH of the environment, then the conjugate base
(anion) form of the species will predominate. Example = CH3COO-
- If its pKa > pH of the environment, then the environment is more
acidic, so its acidic (neutral) form will predominate. Example
CH3COOH
- Weak acids tend to be absorbed in acidic environments, like the
stomach.
- Weak Base
- pKa
- If its pKa < pH of the environment, then the environment is more
basic, so the species will remain in the neutral form. Example =
NH3
- If its pKa > pH of the environment, then the environment is more
acidic, so it will give up its extra H+ to the base, and
the base will exist in its cation form. Example = NH4+
- Weak bases tend to be absorbed in basic environments, like the
duodenum.
DRUG PERMEATION:
- Partition Coefficient: The ratio of lipid solubility to
aqueous solubility. The higher the partition coefficient, the more membrane
soluble is the substance.
- Kidney Glomeruli have the largest pores through which drugs can pass
------> drug filtration.
- Blood Brain Barrier (BBB): Only lipid-soluble
compounds get through the BBB.
- Four components to the blood-brain barrier:
- Tight Junctions in brain capillaries
- Glial cell foot processes wrap around the
capillaries
- Low CSF protein concentration ------> no oncotic pressure for
reabsorbing protein out of the plasma.
- Endothelial cells in the brain contain enzymes that metabolize,
neutralize, many drugs before they access the CSF.
- MAO and COMT are found in brain endothelial cells. They
metabolize Dopamine before it reaches the CSF,
thus we must give L-DOPA in order to get dopamine to the CSF.
- Exceptions to the BBB. Certain parts of the brain are not protected
by the BBB:
- Pituitary, Median Eminence
- Supraventricular areas
- Parts of hypothalamus
- Meningitis: It opens up the blood brain barrier, due to
edema. Thus Penicillin-G can be used to treat meningitis, despite the fact
that it doesn't normally cross the BBB.
- Penicillin-G is also actively pumped back out of
the brain once it has crossed the BBB.
Routes of Administration:
- ORAL
- FIRST-PASS EFFECT: Alteration of drugs in liver via
protal circulation. Some drugs have a high first-pass effect and thus a
lower bioavailability. Know these:
- Morphine
- Imipramine
- Propanolol
- Gastric Emptying: Generally, anything that slows gastric emptying
will slow the absorption of drugs.
- Things that slow gastric emptying: Fats, acidic pH, bulk,
anticholinergics, hypothyroidism, Al(OH)3
- Faster gastric emptying is beneficial for the absorption of
most drugs
- Tetracycline chelates calcium and should
therefore not be given with milk.
- TOPICAL: Lipophilic drugs absorbed through skin.
- Examples: Nicotine patch, nitroglycerine, scopolamine
= anti-histamine given for motion-sickness.
VOLUME OF DISTRIBUTION: The apparent amount of volume that a drug seems
to distribute to.
-
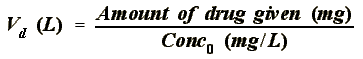
- Sites of Concentration: They can affect the Volume of Distribution
- FAT: Drug concentrates in fat ------> lower concentration of drug in
the plasma ------> high Vd
- BONE: Drug concentrates in bone ------> lower concentration of drug
in the plasma ------> high Vd
- TISSUE: Drug concentrates in tissue ------> lower concentration of
drug in the plasma ------> high Vd
- PLASMA PROTEINS: Drug binds to plasma protein ------> higher
concentration of drug in the plasma ------> low Vd.
- The Vd is based on the total amount of drug
in the plasma -- not just the amount of free drug!
- TRANSCELLULAR: Drug concentrates in non-plasma locations ------>
lower concentration of drug in the plasma ------> high Vd
| Apparent Vd |
Apparent Vd
(L/kg) |
#Liters in 70kg man |
% Total Body Weight |
Example, Explanation |
| Plasma Water |
0.045 L/kg |
3 L |
4.5% |
Plasma-Protein-bound drugs, and large drugs that stay in plasma.
Concentrates in blood and thus has a small Vd.
Example = Heparin |
| Extracellular Water |
0.2 L/kg |
14 L |
20% |
Large water soluble drugs.
Example = Mannitol |
| Total Body Water |
0.6 L/kg |
42 L |
60% |
Small water soluble drugs; rapid equil-ibration between body
compartments.
Example = Ethanol |
| Tissue
Concentration |
>0.7 L/kg |
>42 L |
----- |
Drugs that bind to tissue
Example = chloroquine, which intercalates with DNA
intracellularly.
Vd may be greater than TBW volume, hence some drug must be
bound to plasma.
This is very common and occurs with many drugs. |
- Enterohepatic Circulation: Drugs that are recycled
through the enterohepatic circulation will have a lower concentration of
drug in the plasma, and therefore a higher Vd.
PLASMA PROTEIN BINDING: Two main plasma proteins carry drugs in the blood.
| ALBUMIN |
alpha1-Acid Glycoprotein
OROSOMUCOID |
| Negatively Charged, hence it binds primarily to weak acids. |
Positively Charged, hence it binds primarily to weak bases. |
| Negative acute-phase protein: its synthesis
decreases during time of body insult. |
Positive acute-phase protein: its synthesis
increases during times of body insult. |
| Examples: Phenytoin, Salicylates |
Examples: Quinidine, Propanolol |
|

