- Solvent screening and selection
5.1 Solvent criteria
One of the most important steps in developing a successful
(economical) extractive distillation sequence is selecting a good solvent.
Approaches to the selection of an extractive distillation solvent are discussed
by Berg, Ewell et al. , and Tassions. In general, selection criteria
include the following :
- Should enhance significantly the natural relative volatility of the key
component.
- Should not require an excessive ratio of solvent to nonsolvent (because
of cost of handling in the column and auxiliary equipment.
- Should remain soluble in the feed components and should not lead to the
formation of two phase.
- Should be easily separable from the bottom product.
- Should be inexpensive and readily available.
- Should be stable at the temperature of the distillation and solvent
separation.
- Should be nonreactive with the components in the feed mixture.
- Should have a low latent heat.
- Should be noncorrosive and nontoxic.
Naturally no single solvent or solvent mixture satisfy all
the criteria, and compromises must be reached.
5.2 Solvent screening
Perry's handbook serve as a good reference for the solvent
selection procedure, which can be thought of as a two-step process, i.e.:
5.2.1 First level: Broad screening by functional group or
chemical family
- Homologous series: Select candidate solvent from the high boiling
homologous series of both light and heavy key components.
- Robins Chart: Select candidate solvents from groups in the
Robbins Chart (part of the chart is shown in Table 3) that tend to
give positive (or no) deviations from Raoult's law for the key component
desire in the distillate and negative (or no) deviations for the other key.
- Hydrogen-bonding characteristic: are likely to cause the
formation of hydrogen bonds with the key component to be removed in the
bottoms, or disruption of hydrogen bonds with the key to be removed in the
distillate. Formation and disruption of hydrogen bonds are often associated
with strong negative and positive deviations, respectively from Raoult's
Law.
- Polarity characteristic: Select candidate solvents from chemical
groups that tend to show higher polarity than one key component or lower
polarity than the other key.
5.2.2 Identification of individual candidate solvents
- Boiling point characteristic: Select only candidate solvents that
boil at least 30-40oC above the key components to ensure that the
solvent is relatively nonvolatile and remains largely in the liquid phase.
With this boiling point difference, the solvent should also not form
azeotropes with the other components.
- Selectivity at the infinite dilution: Rank the candidate solvents
according to their selectivity at infinite dilution.
- Experimental measurement of relative volatility: Rank the
candidate solvents by the increase in relative volatility caused by the
addition of the solvent.
Residue curve maps are of limited usefulness at the
preliminary screening stage because there is usually insufficient information
available to sketch the them, but they are valuable and should be sketched or
calculated as part of the second stage of the solvent selection.
6 The scenario of our distillation process
6.1 The azeotropic condition
For our example which deals with the azeotropic mixture
formed between benzene and cyclohexane, we have chosen extractive
distillation (one of the homogeneous azeotropic distillation
methods). The reason of choosing this method is due to the availability of
information regarding this separation technique and its tendency to operate more
efficiently, i.e. in separating and recycling the separating agent. A brief
discussion of the process is given below.
After the mixture exited as the bottom product of the flash
unit, it contains mostly our desire product of cyclohexane and also a
significant amount of unreacted benzene, which is to be recycled back to the
reactor for further conversion. Our main goal now is to further separate the
remaining components in the mixture. As cyclohexane and benzene have been
encounter most of the remaining composition with the mole % of 44.86 and 54.848
respectively (Table 1), we will consider this to be a binary mixture in
our further discussion.
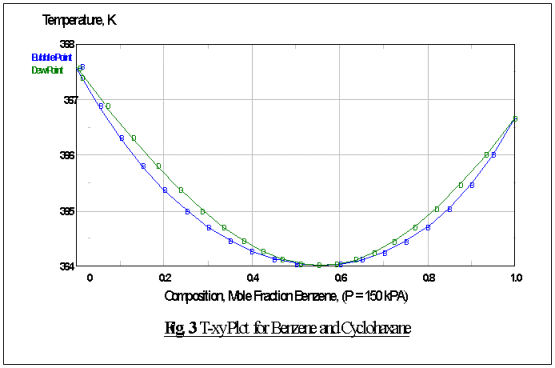
From the process flowsheeting, we would like to operate the
distillation column at the pressure of 150 kPa. At this condition, cyclohexane
and benzene will have boiling points of 94.34oC and 93.49oC
respectively (Fig. 3). This is a typical case where conventional
distillation would struggle to perform the separation of this type of close
boiling mixture. Thus, a special type of distillation technique, i.e. extractive
distillation has been chosen in order to purify the desire product, i.e.
cyclohexane to our desired purity of 99.3%.
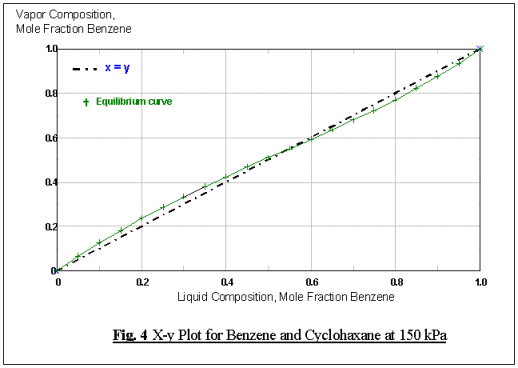
As can be shown from Fig. 3, this binary composition
will form a minimum boiling, homogeneous azeotrope at the temperature of 91oC
and the corresponding composition at this point will be 45.5 mole % for
cyclohexane and 55.5 mole % for benzene (Fig. 4).
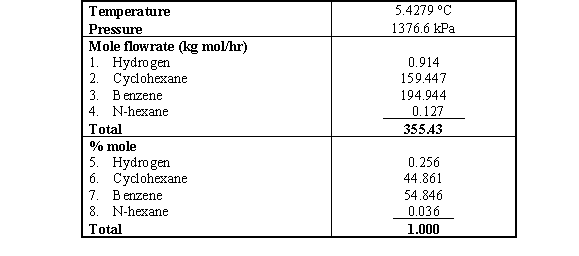
Table 1 Properties of Stream 26 (bottom product of
Flash Drum (F13)
6.2 Solvent selection for benzene-cyclohexane binary
mixture
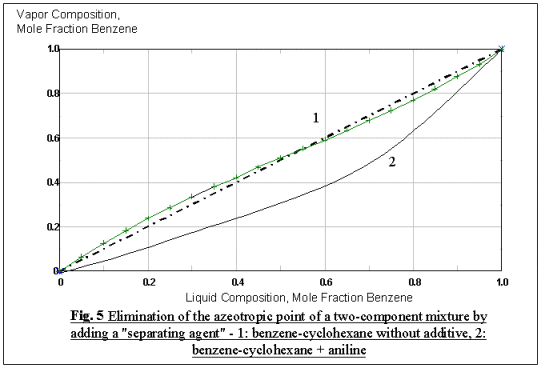
In order to perform a successive extractive distillation, a solvent needs to
be chosen to "break" the azeotrope that forms at the operating pressure of the
distillation column. Recommended solvent for the benzene-cyclohaxane mixture
from the literature,,, is aniline, with a solvent to feed
ratio (S/F) of 4, which will shift the azeotropic point toward the corner of the
high-boiling component cyclohexane, and the equilibrium curve of the original
components fall below the diagonal (Fig. 5).
As was stated in the above section, the primary goal of
solvent selection is to identify a group of feasible solvents to perform a good
separation. The desired product, i.e. cyclohexane should have a purity of above
99% to meet the market standard. Aniline was the first solvent that had been put
to the simulator to be tried out, as it is of the same homologous group as
benzene. As can be shown from the result in Table 2, this solvent will
produce the desire production rate of 150 with the solvent flow rate of 3500,
i.e. a S/F ratio of 9.85. However, the product purity can only reach 70.08% and
this does not meet our product specification. As a result, other solvent may
have to be researched to perform the desire separation.
We will have to perform the solvent selection criteria as
stated in the preceding section. At the column pressure of 150 kPa, cyclohexane
and benzene boil at 94.34oC and 93.49oC respectively and
form a minimum-boiling azeotrope at 91oC. The natural volatility of
the system is benzene > cyclohexane, so the favored solvents most likely will be
those that cause the benzene to be recovered in the distillate. However, in
order to get a better quality of product, we would like to recover cyclohexane
as the distillate rather than from the bottom stream. Thus, solvent to be chosen
should give positive deviations from Raoult's law for cyclohexane and negative
(or zero) deviation for benzene.

Table 2 Result from computer simulation using aniline
as solvent.
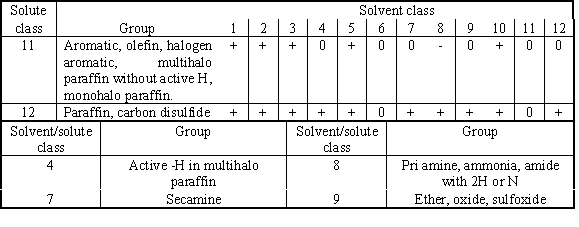
Table 3 Part of Robbins Chart taken from Perry's
Chemical Handbook.
Turning to the Robbins Chart (Table 3), we note
that solvents that may cause the positive deviation for cyclohexane (Class 12)
and negative (or zero) to benzene (Class 11) came from the groups of 4, 7, 8 and
9, which consist of polyol, amine and ether. We further consider the solubility,
the hydrogen bonding effect, and also the homologous characteristic of the
solvent with the corresponding components in the feed mixture. As few candidate
solvents that had been put to the computer simulation, included phenol
(homologous to benzene), 1,2-benzenediol (homologous to benzene, with -OH
group that will produce hydrogen bonding), 1,3-butanediol (with -OH group
that will produce hydrogen bonding), and also 1,2-propanediol (same
characteristic as with 1,3-butanediol). 1,2-propanediol (often
known as propylene glycol), seem to give the most promising results
compared to the other solvents. This result may be caused from the high
solubility of benzene in this solvent and the hydrogen bonding that were formed
between the two constituents. Simulation result of this solvent can be view in
Table 4.
|

