Considering the prismatic element again,
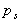 is
the pressure on a plane at any angle is
the pressure on a plane at any angle
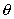 , the
x, y and z directions could be any orientation. The element is so small that it
can be considered a point so the derived expression , the
x, y and z directions could be any orientation. The element is so small that it
can be considered a point so the derived expression
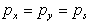 .
indicates that pressure at any point is the same in all directions. .
indicates that pressure at any point is the same in all directions.
(The proof may be extended to include the z axis).
Pressure at any point is the same in all directions.
This is known as Pascal's Law and applies to
fluids at rest.
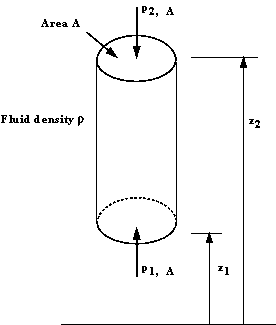
Vertical elemental cylinder of fluid
In the above figure we can see an element of fluid which is a
vertical column of constant cross sectional area, A, surrounded by the same
fluid of mass density
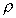 . The
pressure at the bottom of the cylinder is . The
pressure at the bottom of the cylinder is
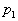 at
level at
level 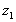 ,
and at the top is ,
and at the top is
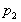 at
level at
level 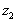 .
The fluid is at rest and in equilibrium so all the forces in the vertical
direction sum to zero. i.e. we have .
The fluid is at rest and in equilibrium so all the forces in the vertical
direction sum to zero. i.e. we have
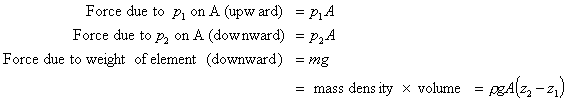
Taking upward as positive, in equilibrium we have
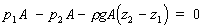
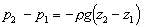
Thus in a fluid under gravity, pressure decreases
with increase in height
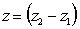 . .
Consider the horizontal cylindrical element of fluid in the
figure below, with cross-sectional area A, in a fluid of density
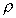 ,
pressure ,
pressure
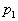 at
the left hand end and pressure at
the left hand end and pressure
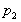 at
the right hand end. at
the right hand end.
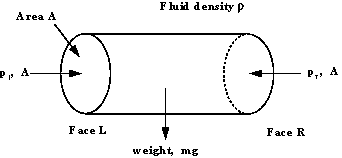
Horizontal elemental cylinder of fluid
The fluid is at equilibrium so the sum of the forces acting in
the x direction is zero.
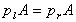
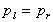
Pressure in the horizontal direction is constant.
This result is the same for any continuous fluid. It is
still true for two connected tanks which appear not to have any direct
connection, for example consider the tank in the figure below.
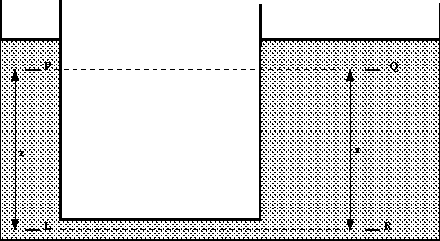
Two tanks of different cross-section connected by a pipe
We have shown above that
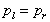 and
from the equation for a vertical pressure change we have and
from the equation for a vertical pressure change we have
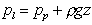
and
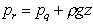
so
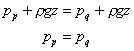
This shows that the pressures at the two equal levels, P and Q
are the same.
Here we show how the above observations for vertical and
horizontal elements of fluids can be generalised for an element of any
orientation.
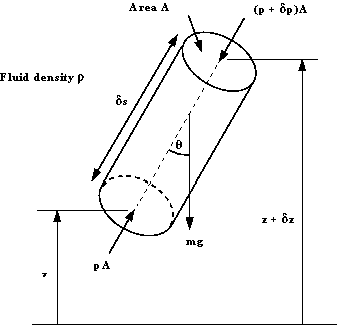
A cylindrical element of fluid at an arbitrary
orientation.
Consider the cylindrical element of fluid in the figure above,
inclined at an angle
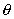 to
the vertical, length to
the vertical, length
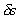 ,
cross-sectional area A in a static fluid of mass density ,
cross-sectional area A in a static fluid of mass density
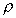 . The
pressure at the end with height . The
pressure at the end with height
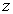 is is
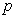 and
at the end of height and
at the end of height
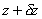 is is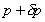 . .
The forces acting on the element are
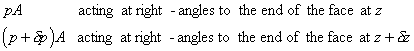

There are also forces from the surrounding fluid acting normal
to these sides of the element.
For equilibrium of the element the resultant of forces in any
direction is zero.
Resolving the forces in the direction along the central axis
gives
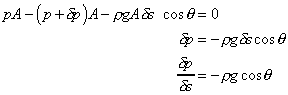
Or in the differential form
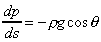
If
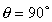 then
s is in the x or y directions, (i.e. horizontal),so then
s is in the x or y directions, (i.e. horizontal),so
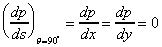
Confirming that pressure on any horizontal plane is zero.
If
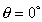 then
s is in the z direction (vertical) so then
s is in the z direction (vertical) so
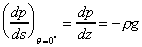
Confirming the result
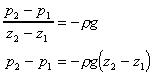
In a static fluid of constant density we have the relationship
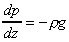 , as
shown above. This can be integrated to give , as
shown above. This can be integrated to give
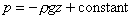
In a liquid with a free surface the pressure at any depth z
measured from the free surface so that z = -h (see the figure below)
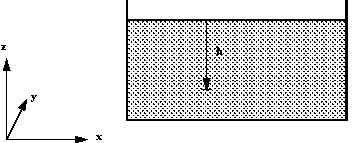
Fluid head measurement in a tank.
This gives the pressure
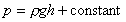
At the surface of fluids we are normally concerned with, the
pressure is the atmospheric pressure,
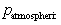 . So . So
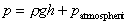
As we live constantly under the pressure of the atmosphere,
and everything else exists under this pressure, it is convenient (and often
done) to take atmospheric pressure as the datum. So we quote pressure as above
or below atmospheric.
Pressure quoted in this way is known as gauge pressure i.e.
Gauge pressure is
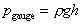
The lower limit of any pressure is zero - that is the pressure
in a perfect vacuum. Pressure measured above this datum is known as absolute
pressure i.e.
Absolute pressure is

As g is (approximately) constant, the gauge pressure
can be given by stating the vertical height of any fluid of density
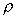 which
is equal to this pressure. which
is equal to this pressure.
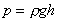
This vertical height is known as head of fluid.
Note: If pressure is
quoted in head, the density of the fluid must also be given.
Example:
We can quote a pressure of
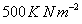 in
terms of the height of a column of water of density, in
terms of the height of a column of water of density,
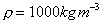 .
Using .
Using 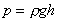 , ,
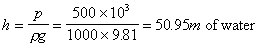
And in terms of Mercury with density,
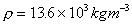 . .
|

