| Recursion |
Recursion may have the following definitions:
-The nested repetition of identical algorithm is recursion.
-It is a technique of defining an object/process by itself.
-Recursion is a process by which a function calls itself repeatedly until some specified condition has been satisfied.
2.4.1 When to use recursion
Recursion can be used for repetitive computations in which each action is stated in terms of previous result. There are two conditions that must be satisfied by any recursive procedure.
- Each time a function calls itself it should get nearer to the solution.
- There must be a decision criterion for stopping the process.
In making the decision about whether to write an algorithm in recursive or non-recursive form, it is always advisable to consider a tree structure for the problem. If the structure is simple then use non-recursive form. If the tree appears quite bushy, with little duplication of tasks, then recursion is suitable.
The recursion algorithm for finding the factorial of a number is given below,
Algorithm : factorial-recursion
Input : n, the number whose factorial is to be found.
Output : f, the factorial of n
Method : if(n=0)
f=1
else
f=factorial(n-1) * n
if end
algorithm ends.
The general procedure for any recursive algorithm is as follows,
- Save the parameters, local variables and return addresses.
- If the termination criterion is reached perform final computation and goto step 3 otherwise perform final computations and goto step 1
 Restore the most recently saved parameters, local variable and return address and goto the latest return address. Restore the most recently saved parameters, local variable and return address and goto the latest return address.
2.4.2 Iteration v/s Recursion
Demerits of recursive algorithms
- Many programming languages do not support recursion, hence recursive mathematical function is implemented using iterative methods.
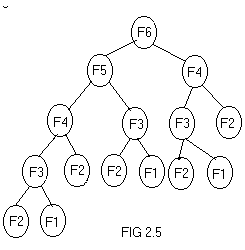
- Even though mathematical functions can be easily implemented using recursion it is always at the cost of execution time and memory space. For example, the recursion tree for generating 6 numbers in a fibonacci series generation is given in fig 2.5. A fibonacci series is of the form 0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,�etc, where the third number is the sum of preceding two numbers and so on. It can be noticed from the fig 2.5 that, f(n-2) is computed twice, f(n-3) is computed thrice, f(n-4) is computed 5 times.
- A recursive procedure can be called from within or outside itself and to ensure its proper functioning it has to save in some order the return addresses so that, a return to the proper location will result when the return to a calling statement is made.
- The recursive programs needs considerably more storage and will take more time.
Demerits of iterative methods
- Mathematical functions such as factorial and fibonacci series generation can be easily implemented using recursion than iteration.
- In iterative techniques looping of statement is very much necessary.
Recursion is a top down approach to problem solving. It divides the problem into pieces or selects out one key step, postponing the rest.
Iteration is more of a bottom up approach. It begins with what is known and from this constructs the solution step by step. The iterative function obviously uses time that is O(n) where as recursive function has an exponential time complexity.
It is always true that recursion can be replaced by iteration and stacks. It is also true that stack can be replaced by a recursive program with no stack.
2.5 Hashing
Hashing is a practical technique of maintaining a symbol table. A symbol table is a data structure which allows to easily determine whether an arbitrary element is present or not.
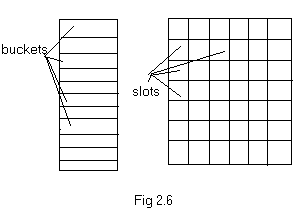
Consider a sequential memory shown in fig 2.6. In hashing technique the address X of a variable x is obtained by computing an arithmetic function (hashing function) f(x). Thus f(x) points to the address where x should be placed in the table. This address is known as the hash address.
The memory used to store the variable using hashing technique is assumed to be sequential. The memory is known as hash table. The hash table is partitioned into several storing spaces called buckets and each bucket is divided into slots (fig 2.6).
If there are b buckets in the table, each bucket is capable of holding s variables, where each variable occupies one slot. The function f(x) maps the possible variable onto the integers 0 through b-1. The size of the space from where the variables are drawn is called the identifier space. Let T be the identifier space, n be the number of variables/identifiers in the hash table. Then, the ratio n/T is called the identifier density and a = n/sb is the loading density or loading factor.
If f(x1)=f(x2), where x1and x2 are any two variables, then x1and x2 are called synonyms. Synonyms are mapped onto the same bucket. If a new identifier is hashed into a already complete bucket, collision occurs.
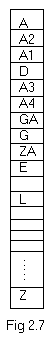
A hashing table with single slot is as given below. Let there be 26 buckets with single slot. The identifier to be stored are GA, D, A, G, L, A2, A1, A3, A4, Z, ZA, E. Let f(x) be the function which maps on to a address equal to the position of the first character of the identifier in the set of English alphabet. The hashing table generated is as shown in fig 2.7.
Time taken to retrieve the identifiers is as follows,
|
Search element (x) |
Search time (t) |
|
GA |
1 |
|
D |
1 |
|
A |
1 |
|
G |
2 |
|
L |
1 |
|
A2 |
2 |
|
A1 |
3 |
|
A3 |
5 |
|
A4 |
6 |
|
Z |
1 |
|
ZA |
10 |
|
E |
6 |
| |
∑t =39 |
Average retrieval time =(∑t)/n.
The average retrieval time entirely depends on the hashing function.
Exercise 2:
What are the serious short comings of the binary search method and sequential search method.
Know more searching techniques involving hashing functions
Implement the algorithms for searching and calculate the complexities
Write an algorithm for the above method of selection sort and implement the same.
Write the algorithm for merge sort method
Take 5 data set of length 10 and hand simulate for each method given above.
Try to know more sorting techniques and make a comparative study of them.
Write an iterative algorithm to find the factorial of a number
Write a recursive and iterative program for reversing a number
Write recursive and iterative program to find maximum and minimum in a list of numbers.
Write an algorithm to implement the hashing technique and implement the same
Hand simulate all algorithms for a 5 datasets.
|

