| Electrical Circuits - Analytical Methods |
Electrical Circuits - Analytical Methods
Introduction
You have learned how to use conductance
matrix analysis in simple circuits. However, the discussion in the first lesson
did not give a formal algorithm for solution of these circuits. Here are our
goals for this lesson.
- Given an electrical circuit
composed of resistors, voltage sources and current sources,
- Be able to write the
conductance matrix representation for the circuit,
- Be able to solve the
conductance matrix-source voltage equation.
A General
Method Of Setting Up Circuit Equations. - Writing The Node Equations
In this section we will consider how
circuit equations are generated and how different elements affect those circuit
equations. We will examine how node equations are
written.
We start by looking at a typical node -
extracted from some larger circuit. That node is shown below.
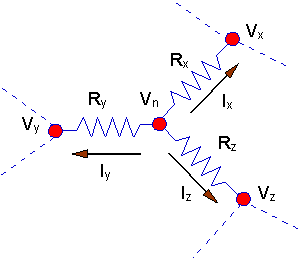 Note the following about this circuit:
Note the following about this circuit:
- The node shown - Node "n" -
is part of a larger circuit. The resistors connected to node "n" are
connected to other nodes through other resistors - shown by dotted lines in
the figure.
- We define currents flowing
out of node "n" as positive when flowing away from the node. Obviously they
can't all be positive, but using this convention helps in developing a
formal methodology for setting up the node equations.
The methodology that we use is as follows.
- Define a voltage at
every node in the circuit. A typical voltage can be denoted
Vn.
- That voltage
symbol,Vn,
denotes the voltage at node "n" measured with respect to ground.
- Note, that at this
point we have to realize that every node voltage might not be an unknown in
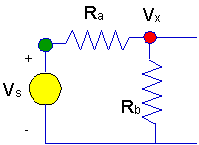
the system of equations that we are developing. For example, in the circuit
below, the voltage at the green node is known to be
Vs,
whereas the voltage,Vx,
is not known a priori.
- When you are setting up a
group of equations to solve, it is important to know how many unknowns
you have (because the level of difficulty of solution is related to the
number of unknowns) and that information is important.
- Having defined a voltage at
every node, it is now possible to write KCL at nodes where the voltage is
not known. The KCL equations have a form that we can discover from the
general node above.

- Then we write KCL at
the node where Vx
appears.
- Finally, we solve whatever
equation results from writing KCL.
We will look at these two steps separately,
and we will work first on the problem of writing KCL at a node.
Writing Node Equations
Here is that node
extracted from a larger circuit.
 Examining the sample node - node "n" - it is
relatively easy to write the KCL equations for the node. Using KCL for the
sample node, we would have:
Ix + Iy
+ Iz = 0
Examining the sample node - node "n" - it is
relatively easy to write the KCL equations for the node. Using KCL for the
sample node, we would have:
Ix + Iy
+ Iz = 0
And, each of the currents can be expressed in
terms of the voltage at the node and the voltage at one of the neighboring
nodes. For example:
Ix = (Vn
-Vx)/Rx
Express every current in that manner, and put
those expressions into the KCL equation:
(Vn -Vx)/Rx
+ (Vn -Vy)/Ry + (Vn
-Vz)/Rz = 0
Notice how this equation plays out. By
defining currents as positive when they are flowing away from the node (i.e.,
the current arrows defining current polarity point away from the node.), every
term that involves Vn turns out
to have a plus sign in the resultant equation. That gives you a way to know
when you have written the equation correctly. There is a payoff to being
systematic and consistent when you write the KCL equations. You will find
almost every textbook that discusses this topic writes the equations this way!
You should adopt that practice as well, and you should never go wrong.
The case of nodes with only resistors
connected is simple enough, but there are special situations that you will need
to take care of. Here are those special cases.
- One of the adjacent nodes
might be connected to a voltage source. Actually, there are two special
cases here because the other end of the voltage source might be connected go
ground - the first case - or it might be connected to still another node -
the second case.
- There might be a current
source connected to the node at which you write KCL.
Let's consider the first case. Here is a
picture of the situation with an adjacent node connected to a
grounded voltage source.
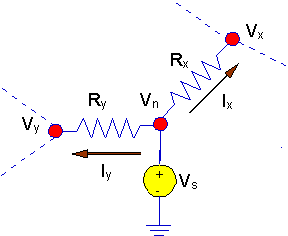
In this situation, KCL is written exactly as it
was before. However, the voltage source serves to fix a node voltage and that
node voltage is no longer a variable with an unknown value. Instead, the
voltage at node 'x' in the figure is known to be Vs.
After you have written KCL at the node, when you go to solve the KCL equations
simultaneously, that known value will appear in a term on the right hand side
(the knowns) of the equation. Thus:
- If there is a grounded source
connected to node "n", then:
- No KCL equation is
written at node "n".
- We have
Vn = Vs.
There is another case in which there is a
voltage source connected between two nodes -
neither of which is ground. In this case the voltage source establishes a
voltage difference between two nodes, and the way this situation is handled is
slightly different.
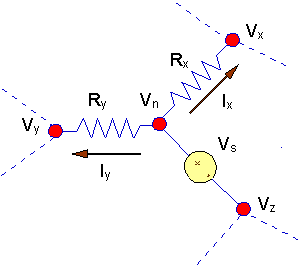
- If there is an ungrounded
source connected between node "n" and node "z", then
- If
Vz can
be found, thenVz
is known from this equation.
- One less KCL equation will be
written for this circuit.
- Then, the approach
would be to write a KCL equation at either node "n" or node "z", and use the
equationVn = Vz
+ Vs to find the voltage at
the other node.
- The implication is that
one less KCL equation will be written.
|

