| Measuring Voltage |
Measuring Voltage
Instruments for Measuring Voltage
In the material above, we assumed that you
would measure voltage with a voltmeter. Actually, there are often numerous
options for the instruments you use to measure voltage. Here are three common
options.
- A Voltmeter
- An Oscilloscope
- An A/D card in a computer
We will examine each of these options separately in
the next section. Before we get there, however, note these common points for
each of these three instruments.
- Each measures voltage.
- To measure voltage, remember
that voltage is an "across" variable. Each instrument will therefore have
two leads to be connected to the circuit where you want to measure voltage,
and those leads should be placed across the two points defining the voltage
you want to measure.
Internal Resistance
Voltmeters (including oscilloscopes, etc.
as voltmeters) will have an effect on any circuit when they are used. Any time
you take a measurement - no matter what the measurement is - you disturb the
thing you are measuring. Attaching a voltmeter to a circuit will change the
circuit - i.e. disturb the circuit - and modify the voltage you are trying to
measure. You just have to ensure that the disturbance is negligible. That's
what we want to look at here.
Let's examine measuring the outut voltage
of a
voltage divider circuit. Here is the circuit.
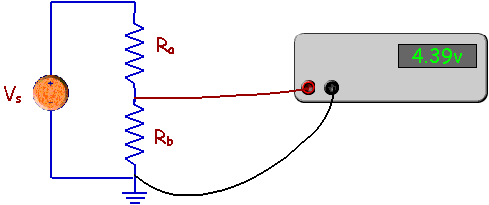
Now, the voltmeter is really equivalent to
a resistor, so we can - for purposes of analysis - replace the voltmeter by its
equivalent resistance. Here is the circuit with the voltmeter equivalent
resistance. (Rm is the resistance of the voltmeter.)
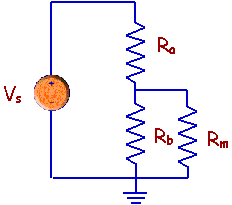
Now, you should be able to see that this
isn't the same circuit that you thought you were measuring. The addition of the
voltmeter resistance changes the circuit and the changed circuit will have a
different output voltage than the original circuit. The question is whether the
output voltage of the changed circuit is significantly different from the output
voltage of the original circuit.
To determine if the output voltage has
changed, you need to consider that the voltmeter and the resistance, Rb,
are now in
parallel. That means that the output of the voltage divider is different.
However, you can compute the output without the meter and with the meter.
Vout = Vin
Rb/( Ra + Rb) - without
the meterand
Vout = Vin
Re/( Ra + Re) - with the
meter, and
Re = Rm
Rb/( Rm + Rb)
These two expressions are very similar, and the
how the close the two voltages will be depends upon how close the equivalent
resistance and the original resistance are. Note that the equivalent parallel
resistance is:
Re = Rm
Rb/( Rm + Rb)
Re = Rb
[Rm/( Rm + Rb)]
So, if the factor multiplying Rb
is close to one, there won't be much difference between the original voltage and
the voltage you have when you attach the voltmeter. In order to be sure that is
true, we need to have the factor multiplying Rb as close to
one as possible.
[Rm/( Rm
+ Rb)] = 1
or at least get as close to 1 as we can. That's
going to happen when the meter resistance is much larger than Rb.
The conclusion that you come to is that
you want the resistance of a voltmeter - any voltmeter, including osciloscopes,
etc. - to be as large as possible. We'll look at typical values for instruments
that are sold as we examine individual instruments.
Voltmeters
Voltmeters are perhaps the commonest or
most widely used instruments for measuring voltage. While there are still many
analog voltmeters, most voltmeters today have digital displays, so that you get
an LCD display with several digits of resolution.
If an instrument has other capabilities
(for example being able to measure current and/or resistance) then it is a
multimeter. If it is a digital multimeter it is
often referred to as a "DMM". A digital voltmeter
can be referred to as a
DVM.
There are several things you will need to
worry about when using a voltmeter or DMM.
- Voltmeters can often measure
either DC or AC voltages.
- When measuring AC
voltages, a voltmeter will give you values for the
RMS value - not the
peak value of the sine wave. And, if the signal isn't sinusoidal,
you may have trouble getting the measured value(s) you want.
- In many instances, it is
possible to connect the voltmeter to a computer. That allows you to import
your data into a computer and then use analysis programs like Mathcad,
Matlab, spreadsheets, etc. to extract information from your data. You may
need to learn how to use those kinds of connections.
- Voltmeters have range
settings. Some common range settings are 0-0.3v, 0-3v, 0-30v, etc. On
lower ranges you will get more accuracy. On digital voltmeters, for example
these ranges are really:
- 0-3.0000 v
- 0-30.000 v
- As you go to higher
ranges you will get as many significant digits in the measured value.
- If you want more
significant digits in a meter the cost will go up, and each additional
digit is more expensive.
- Voltmeters are not
ideal. The most common aspect of a voltmeter that you need to take into
account is the resistance of the voltmeter. Typically a DMM will have a
resistance of 10 MW.
When you connect the voltmeter to a circuit it would be like connecting a 10
MW
resistance to the circuit. In many circuits that won't be a problem because
that will be a negligible disturbance to the circuit.
- Voltmeters measure voltages
that are constant or at least do not change rapidly. A typical digital
voltmeter will measure voltage and display the results, then hold the
results long enough for you to see the number.
The last point in the bullets above has a
hidden question. That question is "What if you have a voltage that changes
rapidly and you want to see details as it changes?". If you have that
situation, a voltmeter may not be your instrument of choice. You may need an
oscilloscope or an A/D card in a computer. That's what we will examine next.
Oscilloscopes
Oscilloscopes can measure time-varying voltages and give you a graph of
voltage vs. time. When you think about how to connect them to a circuit, they
are exactly like voltmeters. You connect an oscilloscope across the two points
where you want to measure the voltage. However, what you get from an
oscilloscope is not what you get from a voltmeter. When you measure a signal
with an oscilioscope, you get a scaled picture of the voltage time-function.
That picture might look like this one if you were measuring a sinusoidal
voltage.
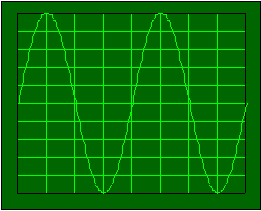
Currently oscilloscopes will also perform some
computations using data taken from the voltage waveform that is presented on the
oscilloscope face. These usually include things like the following.
Also, once those signal parameters are computed and
are in numerical form within the oscilloscope, they can be transmitted - using a
variety of ways - to a computer where you can use a program to compute other
properties you might be interested in. For example, you might capture a
transient temperature and measure the time it takes your temperature control
system to reach a steady state by computing a time constant. You could use any
number of analysis programs for that including Mathcad, Matlab and spreadsheets.
If you want a more complete description of
oscilloscopes, you can go to the lesson on oscilloscopes by
clicking here. (That lesson has a number of interesting simulations you can
try, so that you can learn a little before you go into lab. It also has links
to laboratories that help you learn to use oscilloscopes.)
A/D Boards
You can purchase numerous A/D (short for
Analog-to-Digital Converter) (Click
here to go to the lesson on A/D converters.) converters that come on boards
that plug into computers. And, there are numerous ways to interface with such
boards including at least the following.
- Pre-written programs you can
buy
- Programming in C or C++
- Programs that allow you to
build good-looking GUIs (That's Graphical User Interfaces) including:
- Programming in Visual C++
- Programming in LabView
- Programming in Matlab
- Programming in Visual
Basic
- and others!
The ability to use these boards to get data into a
computer allows you to use analysis programs like Mathcad, Matlab and
spreadsheets to analyze your data, plot it, and to extract other information
from your data.
In many cases you may have
soft instruments on the computer. Soft instruments
are computer programs that simulate voltmeters and oscilloscopes. In other
words, they look and feel like instruments (except that they are interactive
images on a computer screen). They are often designed to look and act like real
instruments as much as possible.
|

